Sulfide Oxidation by O2: Synthesis, Structure and Reactivity of Novel Sulfide-Incorporated Fe(II) Bis(imino)pyridine Complexes
- PMID: 23878411
- PMCID: PMC3712537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.poly.2013.01.043
Sulfide Oxidation by O2: Synthesis, Structure and Reactivity of Novel Sulfide-Incorporated Fe(II) Bis(imino)pyridine Complexes
Abstract
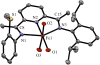
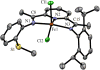
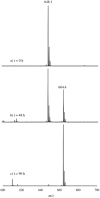
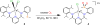
The unsymmetrical iron(II) bis(imino)pyridine complexes [FeII(LN3SMe)(H2O)3](OTf)2 (1), and [FeII(LN3SMe)Cl2] (2) were synthesized and their reactivity with O2 was examined. Complexes 1 and 2 were characterized by single crystal X-ray crystallography, LDI-MS, 1H-NMR and elemental analysis. The LN3SMe ligand was designed to incorporate a single sulfide donor and relies on the bis(imino)pyridine scaffold. This scaffold was selected for its ease of synthesis and its well-precedented ability to stabilize Fe(II) ions. Complexes 1 and 2 ware prepared via a metal-assisted template reaction from the unsymmetrical pyridyl ketone precursor 2-(O=CMe)-6-(2,6-(iPr2-C6H3N=CMe)-C5H3N. Reaction of 1 with O2 was shown to afford the S-oxygenated sulfoxide complex [Fe(LN3S(O)Me)(OTf)]2+(3), whereas compound 2, under the same reaction conditions, afforded the corresponding sulfone complex [Fe(LN3S(O2)Me)Cl]2+ (4).
Keywords: bis(imino)pyridine; dioxygen; iron(II); sulfide; sulfone; sulfoxide.
Figures





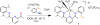
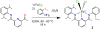


Similar articles
-
Synthesis and ligand non-innocence of thiolate-ligated (N4S) Iron(II) and nickel(II) bis(imino)pyridine complexes.Inorg Chem. 2013 Sep 16;52(18):10467-80. doi: 10.1021/ic4013558. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Inorg Chem. 2013. PMID: 23992096 Free PMC article.
-
O2 activation by bis(imino)pyridine iron(II)-thiolate complexes.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Feb 9;133(5):1274-7. doi: 10.1021/ja109923a. Epub 2011 Jan 5. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21207980 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and electronic structure of cationic, neutral, and anionic bis(imino)pyridine iron alkyl complexes: evaluation of redox activity in single-component ethylene polymerization catalysts.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Oct 27;132(42):15046-59. doi: 10.1021/ja106575b. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20882992
-
Biomimetic aryl hydroxylation derived from alkyl hydroperoxide at a nonheme iron center. Evidence for an Fe(IV)=O oxidant.J Am Chem Soc. 2003 Feb 26;125(8):2113-28. doi: 10.1021/ja028478l. J Am Chem Soc. 2003. PMID: 12590539
-
Preparation of aluminum(III) (bis(amido)pyridine)(thiolate) complexes: unexpected transmetalation mediated by LiAlH(4).Inorganica Chim Acta. 2012 Mar 15;382:19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2011.09.056. Inorganica Chim Acta. 2012. PMID: 22345823 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
X-ray absorption spectroscopic characterization of the diferric-peroxo intermediate of human deoxyhypusine hydroxylase in the presence of its substrate eIF5a.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2016 Sep;21(5-6):605-18. doi: 10.1007/s00775-016-1373-8. Epub 2016 Jul 5. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2016. PMID: 27380180 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Dioxygen by a Mononuclear Nonheme Iron Complex: Sequential Peroxo, Oxo, and Hydroxo Intermediates.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Nov 6;141(44):17533-17547. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b05274. Epub 2019 Oct 24. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 31647656 Free PMC article.
-
A Carboxylate Shift Regulates Dioxygen Activation by the Diiron Nonheme β-Hydroxylase CmlA upon Binding of a Substrate-Loaded Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase.Biochemistry. 2016 Oct 18;55(41):5818-5831. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00834. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27668828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bollinger JM, Jr, Krebs C. J Inorg Biochem. 2006;100:586. - PubMed
-
- Solomon EI, Brunold TC, Davis MI, Kemsley JN, Lee SK, Lehnert N, Neese F, Skulan AJ, Yang YS. J Zhou, Chem Rev. 2000;100:235. - PubMed
-
- Costas M, Mehn MP, Jensen MP, Que L., Jr Chem Rev. 2004;104:939. - PubMed
-
- Koehntop KD, Emerson JP, Que L., Jr J Biol Inorg Chem. 2005;10:87. - PubMed
-
- Neidig ML, Solomon EI. Chem Commun. 2005:5843. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
