Electroacupuncture Attenuates 5'-Guanidinonaltrindole-Evoked Scratching and Spinal c-Fos Expression in the Mouse
- PMID: 23878596
- PMCID: PMC3708416
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/319124
Electroacupuncture Attenuates 5'-Guanidinonaltrindole-Evoked Scratching and Spinal c-Fos Expression in the Mouse
Abstract
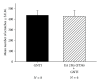
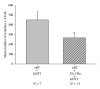
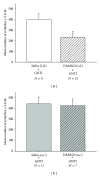
The present study was undertaken to investigate the influence of electroacupuncture (EA) on compulsive scratching in mice and c-Fos expression elicited by subcutaneous (s.c.) administration of a known puritogen, 5'-guanidinonaltrindole (GNTI) to the neck. Application of EA to Hegu (LI4) and Quchi (LI11) acupoints at 2 Hz, but not 100 Hz, attenuated GNTI-evoked scratching. In mice pretreated with the µ opioid receptor antagonist naloxone, EA 2 Hz did not attenuate GNTI-evoked scratching, whereas EA at 2 Hz did attenuate GNTI-evoked scratching in mice pretreated with the κ opioid receptor antagonist nor-binaltorphimine. Moreover, intradermal (i.d.) administration of the selective µ opioid receptor agonist [d-Ala2, N-Me-Phe4, Gly5-ol]-enkephalin acetate (DAMGO) attenuated GNTI-evoked scratching behavior, while s.c. administration of DAMGO was ineffective. GNTI provoked c-Fos expression on the lateral side of the superficial layer of the dorsal horn of the cervical spinal cord. Application of 2 Hz EA to LI4 and LI11 decreased the number of c-Fos positive nuclei induced by GNTI. It may be concluded that application of 2 Hz EA to LI4 and LI11 attenuates scratching behavior induced by GNTI in mice and that the peripheral µ opioid system is involved, at least in part, in the anti-pruritic effects of EA.
Figures







References
-
- Bergasa NV. Update on the treatment of the pruritus of cholestasis. Clinics in Liver Disease. 2008;12(1):219–234. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson CP, Wallengren J. Therapeutic and experimental therapeutic studies on acupuncture and itch: review of the literature. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 2010;24(9):1013–1016. - PubMed
-
- Yosipovitch G, Greaves MW, Schmelz M. Itch. The Lancet. 2003;361(9358):690–694. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

