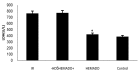
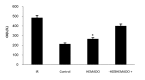
Effect of HEMADO on Level of CK-MB and LDH Enzymes after Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Isolated Rat Heart
- PMID: 23878794
- PMCID: PMC3713869
- DOI: 10.5681/bi.2013.003
Effect of HEMADO on Level of CK-MB and LDH Enzymes after Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Isolated Rat Heart
Abstract
Introduction: Ischemia/Reperfusion (IR) injury mainly causes the increase of enzymes involved in myocytes injury including CK-MB (creatine kinase-MB) isoenzyme and LDH (lactate dehydrogenase). Leakage of CK-MB isoenzyme and LDH from myocardial tissues to blood is indicator of acute myocardial infarction. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of HEMADO on IR injury and its relationship with mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channels (mitoKATP) in rat heart.
Methods: Twenty eight male Wistar rats (250-300g) were divided into four groups (seven members in each group): control (without ischemia), I/R (with ischemia+without HEMADO), ischemia received HEMADO (HEMADO), ischemia received HEMADO and 5-HD (5-hydroxydecanoate, specific mitoKATP channel blocker) (HEMADO+5-HD). The animals were anesthetized and the hearts were quickly removed and mounted on Langendorff apparatus and perfused by Krebs-Henseleit solution under constant pressure and temperature of 37ºC. After 20 minutes of stabilization, ischemic groups were exposed to 40 minutes of global ischemia and consecutive 90 minutes of reperfusion.
Results: IR injury increased the level of LDH and CK-MB in the collected coronary flow during 5 minutes since start of reperfusion. HEMADO reduced the enzymes' levels and using 5-HD abolished the effect of HEMADO.
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that HEMADO could protect the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury by decreasing the CK-MB and LDH levels. The cardioprotective effect of HEMADO may be mediated in part by mitoKATP.
Keywords: Creatine Kinase; HEMADO; Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury; Lactate Dehydrogenase; mitoKATP.
Similar articles
-
[Mechanism of cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury by valsartan: an experiment with isolated rat hearts].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Dec 14;85(47):3350-3. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16409843 Chinese.
-
Sevoflurane postconditioning protects isolated rat hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010 May 20;123(10):1320-8. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010. PMID: 20529589
-
[Protective effect of intralipid on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2008 Apr;20(4):227-30. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2008. PMID: 18419958 Chinese.
-
The effect of acute stress exposure on ischemia and reperfusion injury in rat heart: role of oxytocin.Stress. 2012 Jul;15(4):385-92. doi: 10.3109/10253890.2011.630436. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Stress. 2012. PMID: 22044052
-
Diosgenin-induced protection against myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury is mediated by mitochondrial KATP channels in a rat model.Perfusion. 2015 Oct;30(7):565-71. doi: 10.1177/0267659114566064. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Perfusion. 2015. PMID: 25552273
Cited by
-
Chiral Strategy for Developing High-Performance Polymeric Gadolinium-Based MRI Contrast Agents for Vascular and Tumor Imaging.Chem Biomed Imaging. 2025 Apr 1;3(6):387-397. doi: 10.1021/cbmi.5c00012. eCollection 2025 Jun 23. Chem Biomed Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40575086 Free PMC article.
-
Puerarin inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in myocardial cells via PPARα expression in rats with chronic heart failure.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Nov;18(5):3347-3356. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7984. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Exp Ther Med. 2019. Retraction in: Exp Ther Med. 2025 Jun 30;30(3):166. doi: 10.3892/etm.2025.12916. PMID: 31602208 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Mechanistic investigation of the ameliorative effect of liquiritin on hypoxia/reoxygenation‑induced cardiomyocyte injury based on network pharmacology and in vitro validation.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Jan 29;27(3):117. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12405. eCollection 2024 Mar. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38361515 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Baicalin on Experimental Myocardial Infarction in Rats.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2018 Jul-Aug;33(4):384-390. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2018-0059. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 30184036 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-182-5p alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting GSDMD in mice.Cell Death Discov. 2022 Apr 14;8(1):202. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00909-6. Cell Death Discov. 2022. PMID: 35422485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liem DA, Honda HM, Zhang J, Woo D, Ping P. Past and present course of cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Appl Physiol . 2007;103:2129–36. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. The Global Burden of Disease Study: A useful projection of future global health? . J Public Health Med . 2000;22: 18– 24. - PubMed
-
- Vinten-Johansen J, Zhao ZQ, Jiang R, Zatta AJ, Dobson GP. Preconditioning and postconditioning: Innate cardioprotection from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Appl Physiol . 2007;103:1441–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous