Molecular functions of thyroid hormones and their clinical significance in liver-related diseases
- PMID: 23878812
- PMCID: PMC3708403
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/601361
Molecular functions of thyroid hormones and their clinical significance in liver-related diseases
Abstract
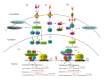
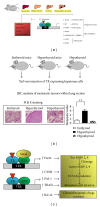
Thyroid hormones (THs) are potent mediators of several physiological processes, including embryonic development, cellular differentiation, metabolism, and cell growth. Triiodothyronine (T3) is the most biologically active TH form. Thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily and mediate the biological functions of T3 via transcriptional regulation. TRs generally form heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) and regulate target genes upon T3 stimulation. Research over the past few decades has revealed that disruption of cellular TH signaling triggers chronic liver diseases, including alcoholic or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Animal model experiments and epidemiologic studies to date imply close associations between high TH levels and prevention of liver disease. Moreover, several investigations spanning four decades have reported the therapeutic potential of T3 analogs in lowering lipids, preventing chronic liver disease, and as anticancer agents. Thus, elucidating downstream genes/signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms of TH actions is critical for the treatment of significant public health issues. Here, we have reviewed recent studies focusing on the roles of THs and TRs in several disorders, in particular, liver diseases. We also discuss the potential therapeutic applications of THs and underlying molecular mechanisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular Functions of Thyroid Hormone Signaling in Regulation of Cancer Progression and Anti-Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 9;20(20):4986. doi: 10.3390/ijms20204986. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31600974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic effects of thyroid hormone derivatives.Thyroid. 2008 Feb;18(2):239-53. doi: 10.1089/thy.2007.0248. Thyroid. 2008. PMID: 18279024 Review.
-
Thyroid hormone action and liver disease, a complex interplay.Hepatology. 2025 Feb 1;81(2):651-669. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000551. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Hepatology. 2025. PMID: 37535802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hypercholesterolemia: Roles of Thyroid Hormones, Metabolites, and Agonists.Thyroid. 2019 Sep;29(9):1173-1191. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0664. Thyroid. 2019. PMID: 31389309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular functions and clinical impact of thyroid hormone-triggered autophagy in liver-related diseases.J Biomed Sci. 2019 Mar 8;26(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0517-x. J Biomed Sci. 2019. PMID: 30849993 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemotherapy resistance and metastasis-promoting effects of thyroid hormone in hepatocarcinoma cells are mediated by suppression of FoxO1 and Bim pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Aug 4;7(8):e2324. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.227. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27490929 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Thyroid Hormones and Synthetic Thyromimetics in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 20;23(3):1102. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031102. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Functions of Thyroid Hormone Signaling in Regulation of Cancer Progression and Anti-Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 9;20(20):4986. doi: 10.3390/ijms20204986. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31600974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothyroidism-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (HIN): Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Options.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 18;21(16):5927. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165927. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32824723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Thyroid Hormones on Lipid Metabolism Pathologies in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Biomedicines. 2022 May 25;10(6):1232. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061232. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang Y-H, Tsai M-M, Lin K-H. Thyroid hormone dependent regulation of target genes and their physiological significance. Chang Gung Medical Journal. 2008;31(4):325–334. - PubMed
-
- Pilo A, Iervasi G, Vitek F, Ferdeghini M, Cazzuola F, Bianchi R. Thyroidal and peripheral production of 3,5,3’-triiodothyronine in humans by multicompartmental analysis. American Journal of Physiology. 1990;258(4, part 1):E715–E726. - PubMed
-
- Tatar E, Sezis Demirci M, Kircelli F, et al. The association between thyroid hormones and arterial stiffness in peritoneal dialysis patients. International Urology and Nephrology. 2011;44(2):601–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

