Hip arthroscopy for extra-articular hip disease
- PMID: 23881610
- PMCID: PMC4094012
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-013-9177-8
Hip arthroscopy for extra-articular hip disease
Abstract
The increasing popularity and success of hip arthroscopy has led to the development of related techniques for treating hip pathologies external to the joint proper. These minimally invasive endoscopic procedures serve in a diagnostic role to complement clinical evaluations and offer a therapeutic alternative to traditional open techniques. The indications for extra-articular hip endoscopy continue to expand. Recent literature describes applications for treating greater trochanteric pain syndrome, internal snapping hip, deep gluteal syndrome, and subspine impingement and for diagnosing and treating extra-articular sources of hip pain in patients who have undergone hip arthroplasty.
Figures

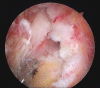
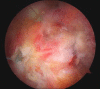
References
-
- Burman MS. Arthrosocpy or the direct visualization of joints: an experimental cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1931;13(4):669–95. - PubMed
-
- Byrd JWT. Routine arthroscopy and access: central and peripheral compartments, iliopsoas bursa, peritrochanteric, and subgluteal spaces. In: Byrd JWT, editor. Operative hip arthroscopy. New York: Springer; 2013. pp. 131–60.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

