Respiratory muscle training for cervical spinal cord injury
- PMID: 23881660
- PMCID: PMC11089516
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008507.pub2
Respiratory muscle training for cervical spinal cord injury
Abstract
Background: Cervical spinal cord injury (SCI) severely comprises respiratory function due to paralysis and impairment of the respiratory muscles. Various types of respiratory muscle training (RMT) to improve respiratory function for people with cervical SCI have been described in the literature. A systematic review of this literature is needed to determine the effectiveness of RMT (either inspiratory or expiratory muscle training) on pulmonary function, dyspnoea, respiratory complications, respiratory muscle strength, and quality of life for people with cervical SCI.
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy of RMT versus standard care or sham treatments in people with cervical SCI.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Injuries and Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Groups' Specialised Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (2012, Issue 1), MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, ISI Web of Science, PubMed, and clinical trials registries (Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry, ClinicalTrials, Controlled Trials metaRegister) on 5 to 8 March 2013. We handsearched reference lists of relevant papers and literature reviews. We applied no date, language, or publication restrictions.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials that involved an intervention described as RMT versus a control group using an alternative intervention, placebo, usual care, or no intervention for people with cervical SCI were considered for inclusion.
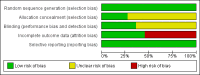
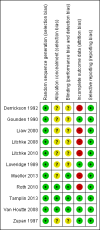
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently selected articles for inclusion, evaluated the methodological quality of the studies, and extracted data. We sought additional information from the trial authors when necessary. We presented results using mean differences (MD) (using post-test scores) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for outcomes measured using the same scale or standardised mean differences (SMD) and 95% CI for outcomes measured using different scales.
Main results: We included 11 studies with 212 participants with cervical SCI. The meta-analysis revealed a statistically significant effect of RMT for three outcomes: vital capacity (MD mean end point 0.4 L, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.69), maximal inspiratory pressure (MD mean end point 10.50 cm/H2O, 95% CI 3.42 to 17.57), and maximal expiratory pressure (MD mean end point 10.31 cm/H2O, 95% CI 2.80 to 17.82). There was no effect on forced expiratory volume in one second or dyspnoea. We could not combine the results from quality of life assessment tools from three studies for meta-analysis. Respiratory complication outcomes were infrequently reported and thus we could not include them in the meta-analysis. Instead, we described the results narratively. We identified no adverse effects as a result of RMT in cervical SCI.
Authors' conclusions: In spite of the relatively small number of studies included in this review, meta-analysis of the pooled data indicates that RMT is effective for increasing respiratory muscle strength and perhaps also lung volumes for people with cervical SCI. Further research is needed on functional outcomes following RMT, such as dyspnoea, cough efficacy, respiratory complications, hospital admissions, and quality of life. In addition, longer-term studies are needed to ascertain optimal dosage and determine any carryover effects of RMT on respiratory function, quality of life, respiratory morbidity, and mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The review authors are currently involved in a research study, which, on completion, may be eligible for inclusion in this review.
Figures





Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008507
References
References to studies included in this review
Derrickson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Derrickson J, Ciesla N, Simpson N, Imle PC. A comparison of two breathing exercise programs for patients with quadriplegia. Physical Therapy 1992;72(11):763‐9. - PubMed
Gounden 1990 {published data only}
-
- Gounden P. Progressive resistive loading on accessory expiratory muscles in tetraplegia. South African Journal of Physiotherapy 1990;46(4):4‐12.
Liaw 2000 {published data only}
-
- Liaw MY, Lin MC, Cheng PT, Wong MK, Tang FT. Resistive inspiratory muscle training: its effectiveness in patients with acute complete cervical cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2000;81(6):752‐6. - PubMed
Litchke 2008 {published data only}
Litchke 2010 {published data only}
-
- Litchke L, Lloyd L, Schmidt E, Russian C, Reardon R. Comparison of two concurrent respiratory resistance devices on pulmonary function and time trial performance of wheel chair athletes. Therapeutic Recreation Journal 2010;44(1):51‐62.
Loveridge 1989 {published data only}
-
- Loveridge B, Badour M, Dubo H. Ventilatory muscle endurance training in quadriplegia: effects on breathing pattern. Paraplegia 1989;27(5):329‐39. - PubMed
Mueller 2013 {published data only}
-
- Mueller G, Hopman MTE, Perret C. Comparison of respiratory muscle training methods in individuals with motor and sensory complete tetraplegia ‐ a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2013;45(3):248‐53. - PubMed
Roth 2010 {published data only}
-
- Roth EJ, Stenson KW, Powley S, Oken J, Primack S, Nussbaum SB, et al. Expiratory muscle training in spinal cord injury: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2010;91(6):857‐61. - PubMed
Tamplin 2013 {published data only}
-
- Tamplin J, Baker F, Grocke D, Brazzale D, Pretto JJ, Ruehland WR, et al. The effect of singing on respiratory function, voice, and mood following quadriplegia: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2013;94(3):426‐34. - PubMed
Van Houtte 2008 {published data only}
-
- Houtte S, Vanlandewijck Y, Kiekens C, Spengler CM, Gosselink R. Patients with acute spinal cord injury benefit from normocapnic hyperpnoea training. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2008;40(2):119‐25. - PubMed
Zupan 1997 {published data only}
-
- Zupan A, Savrin R, Erjavec T, Kralj A, Karcnik T, Skorjanc T, et al. Effects of respiratory muscle training and electrical stimulation of abdominal muscles on respiratory capabilities in tetraplegic patients. Spinal Cord 1997;35(8):540‐5. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alvarez 1981 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez SE, Peterson M, Lunsford BR. Respiratory treatment of the adult patient with spinal cord injury. Physical Therapy 1981;61(12):1737‐45. - PubMed
Biering‐Sorensen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Biering‐Sorensen F, Lehmann Knudsen J, Schmidt A, Bundgaard A, Christensen I. Effect of respiratory training with a mouth‐nose‐mask in tetraplegics. Paraplegia 1991;29(2):113‐9. - PubMed
Crane 1994 {published data only}
-
- Crane L, Klerk K, Ruhl A, Warner P, Ruhl C, Roach KE. The effect of exercise training on pulmonary function in persons with quadriplegia. Paraplegia 1994;32(7):435‐41. - PubMed
Ehrlich 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ehrlich M, Manns PJ, Poulin C. Respiratory training for a person with C3‐C4 tetraplegia. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 1999;45(4):301‐7. - PubMed
Epifanov 1987 {published data only}
-
- Epifanov VA, Zverev VV. Therapeutic physical exercise in the intensive therapy of patients with injuries to the cervical spine and spinal cord. Voprosy Kurortologii, Fizioterapii i Lechebnoi Fizicheskoi Kultury 1987;Mar‐Apr(2):52‐4. - PubMed
Estrup 1986 {published data only}
-
- Estrup C, Lyager S, Noeraa N, Olsen C. Effect of respiratory muscle training in patients with neuromuscular diseases and in normals. Respiration 1986;50(1):36‐43. - PubMed
Fugl‐Meyer 1972 {published data only}
-
- Fugl‐Meyer AR. Respiratory function and training in traumatic spinal cord injuries. Lakartidningen 1972;69(25):3038‐40. - PubMed
Gallego 1993 {published data only}
-
- Gallego J, Perez de la Sota A, Vardon G, Jaeger‐Denavit O. Learned activation of thoracic inspiratory muscles in tetraplegics. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 1993;72(5):312‐7. - PubMed
Goosey‐Tolfrey 2010 {published data only}
-
- Goosey‐Tolfrey V, Foden E, Perret C, Degens H. Effects of inspiratory muscle training on respiratory function and repetitive sprint performance in wheelchair basketball players. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2010;44(9):665‐8. - PubMed
Gross 1980 {published data only}
-
- Gross D, Ladd HW, Riley EJ, Macklem PT, Grassino A. The effect of training on strength and endurance of the diaphragm in quadriplegia. American Journal of Medicine 1980;68(1):27‐35. - PubMed
Hornstein 1986 {published data only}
-
- Hornstein S, Ledsome JR. Ventilatory muscle training in acute quadriplegia. Physiotherapy Canada 1986;38(3):145‐9.
Imamura 1967 {published data only}
-
- Imamura T. The effect of auxiliary respiratory muscular training on breathing exercise in cervical cord injuries. Journal of the Kumamoto Medical Society 1967;41(2):130‐51. - PubMed
Lee 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lee Y, Kim J, Jin Y. The efficacy of pulmonary rehabilitation using a mechanical in‐exsufflator and feedback respiratory training for cervical cord injury patients. Journal of Physical Therapy Science 2012;24(1):89‐92.
Lerman 1987 {published data only}
-
- Lerman RM, Weiss MS. Progressive resistive exercise in weaning high quadriplegics from the ventilator. Paraplegia 1987;25(2):130‐5. - PubMed
Lin 1999 {published data only}
-
- Lin KH, Chuang CC, Wu HD, Chang CW, Kou, YR. Abdominal weight and inspiratory resistance: their immediate effects on inspiratory muscle functions during maximal voluntary breathing in chronic tetraplegic patients. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1999;80(7):741‐5. - PubMed
Lin 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lin VW, Hsiao I N, Zhu E, Perkash I. Functional magnetic stimulation for conditioning of expiratory muscles in patients with spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2001;82(2):162‐6. - PubMed
Metcalf 1966 {published data only}
-
- Metcalf VA. Vital capacity and glossopharyngeal breathing in traumatic quadriplegia. Physical Therapy 1966;46(8):835‐8. - PubMed
Moreno 2012 {published data only}
-
- Moreno MA, Zamuner AR, Paris, JV, Teodori RM, Barros RM. Effects of wheelchair sports on respiratory muscle strength and thoracic mobility of individuals with spinal cord injury. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2012;91(6):470‐7. - PubMed
Moreno 2013 {published data only}
-
- Moreno MA, Paris JV, Sarro KJ, Lodovico A, Silvatti AP, Barros RML. Wheelchair rugby improves pulmonary function in people with tetraplegia after 1 year of training. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 2013;27(1):50‐6. - PubMed
Nygren‐Bonnier 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nygren‐Bonnier M, Wahman K, Lindholm P, Markstrom A, Westgren N, Klefbeck B. Glossopharyngeal pistoning for lung insufflation in patients with cervical spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2009;47(5):418‐22. - PubMed
Rutchik 1998 {published data only}
-
- Rutchik A, Weissman AR, Almenoff PL, Spungen AM, Bauman WA, Grimm DR. Resistive inspiratory muscle training in subjects with chronic cervical spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 1998;79(3):293‐7. - PubMed
Sapienza 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sapienza CM, Wheeler K. Respiratory muscle strength training: functional outcomes versus plasticity. Seminars in Speech & Language 2006;27(4):236‐44. - PubMed
Sutbeyaz 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sutbeyaz ST, Koseoglu BF, Gokkaya NKO. The combined effects of controlled breathing techniques and ventilatory and upper extremity muscle exercise on cardiopulmonary responses in patients with spinal cord injury. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 2005;28(3):273‐6. - PubMed
Uijl 1999 {published data only}
-
- Uijl SG, Houtman S, Folgering HT, Hopman MT. Training of the respiratory muscles in individuals with tetraplegia. Spinal Cord 1999;37(8):575‐9. - PubMed
Valent 2009 {published data only}
-
- Valent LJ, Dallmeijer AJ, Houdijk H, Slootman HJ, Janssen TW, Post MW, et al. Effects of hand cycle training on physical capacity in individuals with tetraplegia: a clinical trial. Physical Therapy 2009;89(10):1051‐60. - PubMed
Walker 1987 {published data only}
-
- Walker J, Cooney M. Improved respiratory function in quadriplegics after pulmonary therapy and arm ergometry. New England Journal of Medicine 1987;316(8):486‐7. - PubMed
Wang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wang T‐G, Wang Y‐H, Tang F‐T, Lin K‐H, Lien IN. Resistive inspiratory muscle training in sleep‐disordered breathing of traumatic tetraplegia. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2002;83(4):491‐6. - PubMed
Additional references
ATS/ERS 2002
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS statement on respiratory muscle testing. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2002;166:518‐624. - PubMed
ATS/ERS 2005
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS Taskforce: Standardization of spirometry. European Respiratory Journal 2005;26:319‐38.
Brooks 2005
-
- Brooks D, O'Brien K, Geddes EL, Crowe J, Reid D. Is inspiratory muscle training effective for individuals with cervical spinal cord injury? A qualitative systematic review. Clinical Rehabilitation 2005; Vol. 19, issue 3:237‐46. - PubMed
Brown 2006
Cardozo 2007
Chen 1990
-
- Chen CF, Lien IN, Wu MC. Respiratory function in patients with spinal cord injuries: effects of posture. Paraplegia 1990; Vol. 28, issue 2:81‐6. - PubMed
DeVivo 1999
-
- DeVivo MJ, Krause S, Lammertse DP. Recent trends in mortality and causes of death among persons with spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1999; Vol. 80, issue 11:1411‐9. [PUBMED: 10569435] - PubMed
Estenne 1987
-
- Estenne M, Troyer A. Mechanism of the postural dependence of vital capacity in tetraplegic subjects. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1987;135(2):367‐71. - PubMed
Estenne 1989
-
- Estenne M, Knoop C, Vaerenbergh J, Heilporn A, Troyer A. The effect of pectoralis muscle training in tetraplegic subjects. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1989; Vol. 139, issue 5:1218‐22. - PubMed
Fishburn 1990
-
- Fishburn MJ, Marino RJ, Ditunno JF. Atelectasis and pneumonia in acute spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1990; Vol. 71:197‐200. - PubMed
Fugl‐Meyer 1984
-
- Fugl‐Meyer AR, Grimby G. Respiration in tetraplegia and in hemiplegia: a review. International Rehabilitation Medicine 1984; Vol. 6, issue 4:186‐90. - PubMed
Fujiwara 1999
-
- Fujiwara T, Hara Y, Chino N. Expiratory function in complete tetraplegics: study of spirometry, maximal expiratory pressure, and muscle activity of pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi muscles. American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1999; Vol. 78, issue 5:464‐73. - PubMed
Hart 2005
-
- Hart N, Laffont I, Perez de la Sota A, Lejaille M, Madadou G, Polkey MI, et al. Respiratory effects of combined truncal and abdominal support in patients with spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2005;86(7):1447‐51. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Reines 1987
-
- Reines HH, Harris RC. Pulmonary complications of acute spinal cord injuries. Neurosurgery 1987; Vol. 21:193‐6. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Rodriguez‐Roisin 2009
-
- Rodriguez‐Roisin R, Anzueto A, Bourbeau J, Calverly P, deGuia TS, Fukuchi Y, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Executive Summary [updated 2009]. www.goldcopd.org (accessed 14 July 2013).
Sale 1988
-
- Sale DG. Neural adaptation to resistance exercise. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 1988; Vol. 20:S135‐45. - PubMed
Sheel 2008
van den Berg 2010
-
- Berg ME, Castellote JM, Pedro‐Cuesta J, Mahillo‐Fernandez I. Survival after spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Journal of Neurotrauma 2010;27:1517‐28. - PubMed
Van Houtte 2006
-
- Houtte S, Vanlandewijck Y, Gosselink R. Respiratory muscle training in persons with spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Respiratory Medicine 2006; Vol. 100, issue 11:1886‐95. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

