Topical application of tranexamic acid for the reduction of bleeding
- PMID: 23881695
- PMCID: PMC12053458
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010562.pub2
Topical application of tranexamic acid for the reduction of bleeding
Abstract
Background: Intravenous tranexamic acid reduces bleeding in surgery, however, its effect on the risk of thromboembolic events is uncertain and an increased risk remains a theoretical concern. Because there is less systemic absorption following topical administration, the direct application of tranexamic acid to the bleeding surface has the potential to reduce bleeding with minimal systemic effects.
Objectives: To assess the effects of the topical administration of tranexamic acid in the control of bleeding.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Injuries Group Specialised Register; Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in The Cochrane Library; Ovid MEDLINE®, Ovid MEDLINE® In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE® Daily and Ovid OLDMEDLINE®; Embase Classic + Embase (OvidSP); PubMed and ISI Web of Science (including Science Citation Index Expanded and Social Science Citation Index (SCI-EXPANDED & CPCI-S)). We also searched online trials registers to identify ongoing or unpublished trials. The search was run on the 31st May 2013.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials comparing topical tranexamic acid with no topical tranexamic acid or placebo in bleeding patients.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors examined the titles and abstracts of citations from the electronic databases for eligibility. Two authors extracted the data and assessed the risk of bias for each trial. Outcome measures of interest were blood loss, mortality, thromboembolic events (myocardial infarction, stroke, deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) and receipt of a blood transfusion.
Main results: We included 29 trials involving 2612 participants. Twenty-eight trials involved patients undergoing surgery and one trial involved patients with epistaxis (nosebleed). Tranexamic acid (TXA) reduced blood loss by 29% (pooled ratio 0.71, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.69 to 0.72; P < 0.0001). There was uncertainty regarding the effect on death (risk ratio (RR) 0.28, 95% CI 0.06 to 1.34; P = 0.11), myocardial infarction (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.04 to 3.08; P = 0.33), stroke (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.96; P = 0.49), deep vein thrombosis (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.31 to 1.57; P = 0.38) and pulmonary embolism (RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.09 to 3.15; P = 0.48). TXA reduced the risk of receiving a blood transfusion by a relative 45% (RR 0.55, 95% CI 0.55 to 0.46; P < 0.0001). There was substantial statistical heterogeneity between trials for the blood loss and blood transfusion outcomes.
Authors' conclusions: There is reliable evidence that topical application of tranexamic acid reduces bleeding and blood transfusion in surgical patients, however the effect on the risk of thromboembolic events is uncertain. The effects of topical tranexamic acid in patients with bleeding from non-surgical causes has yet to be reliably assessed. Further high-quality trials are warranted to resolve these uncertainties before topical tranexamic acid can be recommended for routine use.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures
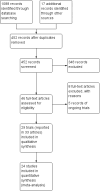

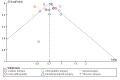

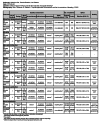
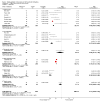






Comment in
-
Cochrane in CORR ®: Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid for the Reduction of Bleeding (Review).Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Jan;475(1):21-26. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-5112-9. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 27709420 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abdullah 2012 {published data only}
-
- Abdullah A, Javed A. Does topical tranexamic acid reduce post‐turp hematuria: A double blind randomized control trial. Urology 2012;80(3):S221‐2.
Abul‐Azm 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Abul‐Azm A, Abdullah KM. Effect of topical tranexamic acid in open heart surgery. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2006;23:380‐4. - PubMed
Albirmawy 2013 {published data only}
-
- Albirmawy OA, Saafan ME, Shehata EM, Basuni AS, Eldaba AA. Topical application of tranexamic acid after adenoidectomy: a double‐blind, prospective, randomized, controlled study. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 2013;77(7):1139‐42. - PubMed
Alshryda 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Alshryda S, Mason J, Sarda P, Nargol A, Maheswaran S, Tulloch C, et al. Topical (intra‐articular) tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates following total knee replacement: a randomised controlled trial (TRANX‐K). Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery in press. - PubMed
Athanasiadis 2007 {published data only}
-
- Athanasiadis T, Beule AG, Wormald PJ. Effects of topical antifibrinolytics in endoscopic sinus surgery: a pilot randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Rhinology 2007; Vol. 21:737‐42. - PubMed
Baric 2007 {published data only}
-
- Baric D, Biocina B, Unic D, Sutlic Z, Rudez I, Vrca V B, et al. Topical use of antifibrinolytic agents reduces postoperative bleeding: a double‐blind, prospective, randomized study. European Journal of Cardio‐thoracic Surgery 2007;31:366‐71. - PubMed
Blinder 1999 {published data only}
-
- Blinder D, Manor Y, Martinowitz U, Taicher S, Hashomer T. Dental extractions in patients maintained on continued oral anticoagulant: comparison of local hemostatic modalities. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontics 1999;88(2):137‐40. - PubMed
Canata 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Canata GL, Casale V, Chiey A. Management of post‐operative pain and bleeding in knee replacement. Journal of Orthopaedic Traumatology 2012;13 Suppl 1:S25‐55.
De Bonis 2000 {published data only}
-
- Bonis M, Cavaliere F, Alessandrini F, Lapenna E, Santarelli F, Moscato U, et al. Topical use of tranexamic acid in coronary artery bypass operations: a double‐blind, prospective, randomized, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2000;119:575‐80. - PubMed
Dell'Amore 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dell'Amore A, Caroli G, Nizar A, Cassanelli N, Luciano G, Greco D, et al. Can topical application of tranexamic Acid reduce blood loss in thoracic surgery? A prospective randomised double blind investigation. Heart, Lung & Circulation 2012;21:706‐10. - PubMed
Fawzy 2009 {published and unpublished data}
Georgiadis 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Georgiadis AG, Muh S, Weir RM, Silverton C, Laker MW. Topical tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a double‐blind, randomized placebo controlled trial (paper 433). American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual Meeting March, 2013.
-
- Georgiadis AG, Muh SJ, Silverton CD, Weir RM, Laker MW. A prospective double‐blind place controlled trial of topical tranexamic acid. Journal of Arthroplasty in press. - PubMed
Gersel‐Pedersen 1979 {published data only}
-
- Gersel‐Pedersen N. Tranexamic acid in alveolar sockets in the prevention of alveolitis sicca dolorosa. International Journal of Oral Surgery 1979;8:421‐9. - PubMed
Ishida 2011 {published data only}
Jabalameli 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jabalameli M, Zakeri K. Evaluation of topical tranexamic acid on intraoperative bleeding in endoscopic sinus surgery. Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences 2006;31(4):221‐3.
Kaewpradub 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kaewpradub P, Apipan B, Rummasak D. Does tranexamic acid in an irrigating fluid reduce intraoperative blood loss in orthognathic surgery? A double‐blind, randomized clinical trial. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2011;69(6):186‐9. - PubMed
Krohn 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Krohn CD, Sorensen R, Lange JE, Riise R, Bjornsen S, Brosstad F. Tranexamic acid given into the wound reduces postoperative blood loss by half in major orthopaedic surgery. European Journal of Surgery 2002;Suppl 588:57‐61. - PubMed
Kurt 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kurt T. Evaluation of the effects of systemic or topical use of tranexamic acid and aprotinin on the blood loss and the used amount of blood products following cardiopulmonary bypass surgery [KLİNİĞİMİZDE YAN YANA ANASTAMOZ TEKNİĞİ KULLANILARAKOLUŞTURULAN HEMODİALİZ AMAÇLI ARTERİYOVENÖZ FİSTÜLLERİNRETROSPEKTİF DEĞERLENDİRİLMESİ]. Anatolian Journal of Clinical Investigation 2011;5(3):116‐21.
Nouraei 2013 {published data only}
-
- Nouraei M, Gholipour Baradari A, Ghafari R, Habibi MR, Emami Zeydi A, Sharifi N. Decreasing blood loss and the need for transfusion after CABG surgery: A double‐blind randomized clinical trial of topical tranexamic acid. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2013;43(2):273‐8.
Ramstrom 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ramstrom G, Sindet‐Pedersen S, Hall G, Blomback M, Alander U. Prevention of postsurgical bleeding in oral surgery using tranexamic acid without dose modification of oral anticoagulants. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1993;51(11):1211‐6. - PubMed
Roy 2012 {published data only}
-
- Roy SP, Tanki UF, Dutta A, Jain SK, Nagi ON. Efficacy of intra‐articular tranexamic acid in blood loss reduction following primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2012;20(12):2494‐501. - PubMed
Saberi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Saberi H, Miri SM, Namdar MP. The effects of topically applied tranexamic acid on reduction of postlaminectomy hemorrhage. Tehran University Medical Journal 2010;68:527‐33.
Sa‐Ngasoongsong 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sa‐Ngasoongsong P, Channoom T, Kawinwonggowit V, Woratanarat P, Chanplakorn P, Wibulpolprasert B, et al. Postoperative blood loss reduction in computer‐assisted surgery total knee replacement by low dose intra‐articular tranexamic acid injection together with 2‐hour clamp drain: a prospective triple‐blinded randomized controlled trial. Orthopedic Reviews 2011;3:e12. - PMC - PubMed
Seo 2012 {published data only}
-
- Seo JG, Moon YW, Park SH, Kim SM, Ko KR. The comparative efficacies of intra‐articular and IV tranexamic acid for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy 2012 June 24 [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
Sindet‐Pedersen 1989 {published data only}
-
- Sindet‐Pedersen S, Ramstrom G, Bernvil S, Blomback M. Hemostatic effect of tranexamic acid mouthwash in anticoagulant‐treated patients undergoing oral surgery. New England Journal of Medicine 1989:840‐3. - PubMed
Tibbelin 1995 {published data only}
-
- Tibbelin A, Aust R, Bende M, Holgersson M, Petruson B, Rundcrantz H, Alander U. Effect of local tranexamic acid gel in the treatment of epistaxis. ORL; Journal for oto‐rhino‐laryngology and its related specialties 1995;57:207‐9. - PubMed
Van Elst 2013 {published data only}
-
- Elst C, Vanbiervliet J, Simon JP, Corten K. The effect of topical application of tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty through the direct anterior apporach. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual Meeting. March, 2013.
Wong 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Abrishami A. Timing and volume of topical tranexamic acid administration for postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia. Springer New York, 2010:S142‐3.
-
- Abrishami A, Wong J, El‐Beheiry H, Hasan SM, Chung F. Intra‐articular application of tranexamic acid for perioperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2009;56:S138.
-
- Wong J, Abrishami A, Silva Y, Hasan SM, Mahomed N, Chung F. A randomized controlled trial of topical tranexamic acid for postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2009;108:S‐22.
-
- Wong J, Abrishami A, Beheiry H, Mahomed NN, Roderick Davey J, Gandhi R, et al. Topical application of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American volume 2010; Vol. 92:2503‐13. - PubMed
Yasim 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yasim A, Aşik R, Atahan E. [Effects of topical applications of aprotinin and tranexamic acid on blood loss after open heart surgery]. [Anatolian Journal of Cardiology] 2005;5:36‐40. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bernardoni‐Socorro 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bernardoni‐Socorro C, Arteaga‐Vizcaino M, Villamizar Y, Diez‐Ewald M, Vizcaino‐Salazar G, Torres‐Guerra E, et al. Mouthwash with tranexamic acid in patients under oral anticoagulant therapy during dental surgery. [Spanish]. Investigacion Clinica 1998;39:77‐83. - PubMed
Borea 1993 {published data only}
-
- Borea G, Montebugnoli L, Capuzzi P, Magelli C. Tranexamic acid as a mouthwash in anticoagulant‐treated patients undergoing oral surgery. An alternative method to discontinuing anticoagulant therapy. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontics 1993;75(1):29‐31. - PubMed
Carter 2003 {published data only}
-
- Carter G, Goss AN. Tranexamic acid mouthwash ‐ A prospective randomized study of a 2‐day regimen vs 5‐day regimen to prevent postoperative bleeding in anticoagulated patients requiring dental extractions. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2003;32:504‐7. - PubMed
Falbe‐Hansen 1974 {published data only}
-
- Falbe‐Hansen J, Jacobsen B, Lorenzen E. Local application of an antifibrinolytic in tonsillectomy. A double‐blind study. The Journal of Laryngology and Otology 1974; Vol. 88:565‐8. - PubMed
Hegde 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hegde C, Wasnik S, Kulkarni S, Pradhan S, Shetty V. Simultaneous bilateral computer assisted total knee arthroplasty: The effect of intravenous or intraarticular tranexamic acid. Journal of Arthroplasty 2013 Apr 30 [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
Maniar 2012 {published data only}
Mutsuzaki 2012 {published data only}
Timocin 1996 {published data only}
-
- Timocin N, Kocak H, Gurkan B, Oner B. Effect of tranexamic acid (transamine) mouthwash after dental extraction in patients who received anticoagulant agents. [Turkish]. Istanbul Tip Fakultesi Mecmuasi 1996;59:37‐40.
References to ongoing studies
NCT01260818 {published data only}
-
- NCT01260818. Prospective Randomized Trial Comparing Topical Tranexamic Acid Plus Standard Of Care Versus Standard Of Care For The Reduction Of Blood Loss Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Surgery. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01260818.
NCT01519245 {published data only}
-
- NCT01519245. Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid to Reduce Post‐operative Bleeding in Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01519245.
NCT01683955 {published data only}
-
- NCT01683955. Topical Tranexamic Acid and Acute Blood Loss in Total Hip Arthroplasty. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01683955.
NCT01727843 {published data only}
-
- NCT01727843. Phase III Examining the Topical Application of Tranexamic Acid and Postoperative Blood Loss in Femoral Neck Fractures: a Randomized Control Trial. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01727843.
TRANX‐H {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN59245192. Topical tranexamic acid in total hip replacement. http://www.controlled‐trials.com/ISRCTN59245192.
Additional references
AbouZahr 2003
-
- AbouZahr C. Global burden of maternal death and disability. British Medical Bulletin 2003;67:1‐11. - PubMed
Almer 1992
-
- Almer S, Andersson T, Ström M. Pharmacokinetics of tranexamic acid in patients with ulcerative colitis and in healthy volunteers after the single instillation of 2g rectally. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1992;32:49‐54. - PubMed
CRASH‐2 Collaborators 2011
-
- CRASH‐2 collaborators, Roberts I, Shakur H, Afolabi A, Brohi K, Coats T, et al. The importance of early treatment with tranexamic acid in bleeding trauma patients: an exploratory analysis of the CRASH‐2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2011;377(9771):1096‐101. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG on behalf of the CSMG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Goodnough 2008
-
- Goodnough L, Shander A. Risk and complications of blood transfusions: optimizing outcomes for patients with chemotherapy‐induced anemia. John Hopkins Advanced Studies in Medicine 2008;8(10):357‐62.
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC on behalf of the CSMG and the CBMG. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG on behalf of the CSMG. Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Ker 2012
Ker 2013
-
- Ker K, Prieto‐Merino D, Roberts I. Systematic review, meta‐analysis and meta‐regression of the effect of tranexamic acid on surgical blood loss. British Journal of Surgery 2013 Jul 9 [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
McCormack 2012
-
- McCormack PL. Tranexamic acid: a review of its use in the treatment of hyperfibrinolysis. Drugs 2012;72(5):585‐617. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Shander 2011
-
- Shander A, Javidroozi M, Ozawa S, Hare GMT. What is really dangerous: anaemia or transfusion?. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2011;107 Suppl 1:i41‐59. - PubMed
Sindet‐Pedersen 1987
-
- Sindet‐Pedersen S. Distribution of tranexamic acid to plasma and saliva after oral administration and mouth rinsing: a pharmacokinetic study. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1987;27:1005‐8. - PubMed
van der Werf 2003
-
- Werf MJ, Vlas SJ, Brooker S, Looman CWN, Nagelkerke NJD, Habbema JDF, et al. Quantification of clinical morbidity associated with schistosome infection in sub‐Saharan Africa. Acta Tropica 2003;86:125‐39. - PubMed
van Leerdam 2008
-
- Leerdam ME. Epidemiology of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Gastroenterology 2008;22(2):209‐24. - PubMed
Weiser 2008
-
- Weiser TG, Regenbogen SE, Thompson KD, Haynes AB, Lipsitz SR, Berry WR, et al. An estimation of the global volume of surgery: a modelling strategy based on available data. Lancet 2008;372(9633):139‐44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

