Mental health collaborative care and its role in primary care settings
- PMID: 23881714
- PMCID: PMC3759986
- DOI: 10.1007/s11920-013-0383-2
Mental health collaborative care and its role in primary care settings
Abstract
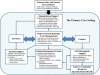
Collaborative care models (CCMs) provide a pragmatic strategy to deliver integrated mental health and medical care for persons with mental health conditions served in primary care settings. CCMs are team-based intervention to enact system-level redesign by improving patient care through organizational leadership support, provider decision support, and clinical information systems, as well as engaging patients in their care through self-management support and linkages to community resources. The model is also a cost-efficient strategy for primary care practices to improve outcomes for a range of mental health conditions across populations and settings. CCMs can help achieve integrated care aims underhealth care reform yet organizational and financial issues may affect adoption into routine primary care. Notably, successful implementation of CCMs in routine care will require alignment of financial incentives to support systems redesign investments, reimbursements for mental health providers, and adaptation across different practice settings and infrastructure to offer all CCM components.
Figures
References
-
- The global burden of disease: 2004 update. World health Organization; Geneva: 2008.
-
- Kessler RC, Wang PS. The descriptive epidemiology of commonly occurring mental disorders in the United States. Annu Rev Public Health. 2008;29:115–29. - PubMed
-
- Baumeister H, Hutter N. Collaborative care for depression in medically ill patients. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2012;25(5):405–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical