Genetic heterogeneity and consanguinity lead to a "double hit": homozygous mutations of MYO7A and PDE6B in a patient with retinitis pigmentosa
- PMID: 23882135
- PMCID: PMC3718492
Genetic heterogeneity and consanguinity lead to a "double hit": homozygous mutations of MYO7A and PDE6B in a patient with retinitis pigmentosa
Abstract
Purpose: Retinitis pigmentosa (RP), the most genetically heterogeneous disorder in humans, actually represents a group of pigmentary retinopathies characterized by night blindness followed by visual-field loss. RP can appear as either syndromic or nonsyndromic. One of the most common forms of syndromic RP is Usher syndrome, characterized by the combination of RP, hearing loss, and vestibular dysfunction.
Methods: The underlying cause of the appearance of syndromic and nonsyndromic RP in three siblings from a consanguineous Israeli Muslim Arab family was studied with whole-genome homozygosity mapping followed by whole exome sequencing.
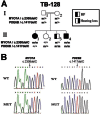
Results: THE FAMILY WAS FOUND TO SEGREGATE NOVEL MUTATIONS OF TWO DIFFERENT GENES: myosin VIIA (MYO7A), which causes type 1 Usher syndrome, and phosphodiesterase 6B, cyclic guanosine monophosphate-specific, rod, beta (PDE6B), which causes nonsyndromic RP. One affected child was homozygous for both mutations. Since the retinal phenotype seen in this patient results from overlapping pathologies, one might expect to find severe retinal degeneration. Indeed, he was diagnosed with RP based on an abnormal electroretinogram (ERG) at a young age (9 months). However, this early diagnosis may be biased, as two of his older siblings had already been diagnosed, leading to increased awareness. At the age of 32 months, he had relatively good vision with normal visual fields. Further testing of visual function and structure at different ages in the three siblings is needed to determine whether the two RP-causing genes mutated in this youngest sibling confer increased disease severity.
Conclusions: This report further supports the genetic heterogeneity of RP, and demonstrates how consanguinity could increase intrafamilial clustering of multiple hereditary diseases. Moreover, this report provides a unique opportunity to study the clinical implications of the coexistence of pathogenic mutations in two RP-causative genes in a human patient.
Figures

References
-
- Reiners J, Nagel-Wolfrum K, Jurgens K, Marker T, Wolfrum U. Molecular basis of human Usher syndrome: deciphering the meshes of the Usher protein network provides insights into the pathomechanisms of the Usher disease. Exp Eye Res. 2006;83:97–119. - PubMed
-
- Friedman TB, Schultz JM, Ahmed ZM, Tsilou ET, Brewer CC. Usher syndrome: hearing loss with vision loss. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;70:56–65. - PubMed
-
- Riazuddin S, Belyantseva IA, Giese AP, Lee K, Indzhykulian AA, Nandamuri SP, Yousaf R, Sinha GP, Lee S, Terrell D, Hegde RS, Ali RA, Anwar S, Andrade-Elizondo PB, Sirmaci A, Parise LV, Basit S, Wali A, Ayub M, Ansar M, Ahmad W, Khan SN, Akram J, Tekin M, Riazuddin S, Cook T, Buschbeck EK, Frolenkov GI, Leal SM, Friedman TB, Ahmed ZM. Alterations of the CIB2 calcium- and integrin-binding protein cause Usher syndrome type 1J and nonsyndromic deafness DFNB48. Nat Genet. 2012;44:1265–71. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
