Adding diet and exercise counseling to the health promotion plan alleviates anthropometric and metabolic complications in patients with metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 23882148
- PMCID: PMC3698469
- DOI: 10.4137/NMI.S9683
Adding diet and exercise counseling to the health promotion plan alleviates anthropometric and metabolic complications in patients with metabolic syndrome
Abstract
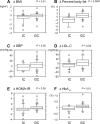
We investigated the effects of individual (IC) and group (GC) diet and exercise counseling in men with metabolic syndrome. Participants received exercise instruction and exercise load was monitored. IC participants received individual diet counseling sessions and general consultations at baseline and monthly. GC participants received a group diet counseling session at baseline and general consultations at baseline and monthly. In the IC group, body mass index (BMI) percent body fat, waist circumference, diastolic blood pressure, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c, and liver function levels were reduced significantly after 3 months, whereas in the GC group, waist circumference and levels of liver function were reduced. Exercise load was negatively correlated with change in BMI and waist circumference in the IC group, and positively correlated with changes in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in all subjects and in the GC group. Diet and exercise counseling, especially IC, may benefit patients with metabolic syndrome.
Keywords: counsel; diet; exercise; metabolic syndrome; waist circumference.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of behavioral counseling on cardiometabolic biomarkers: A longitudinal analysis of the Japanese national database.Prev Med. 2018 Aug;113:116-121. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.05.016. Epub 2018 May 22. Prev Med. 2018. PMID: 29758304
-
A randomized controlled trial of therapeutic lifestyle modification in rural women with metabolic syndrome: a pilot study.Metabolism. 2008 Feb;57(2):255-61. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2007.09.009. Metabolism. 2008. PMID: 18191057 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of community-based exercise intervention programme in obese adults with metabolic syndrome.J Clin Nurs. 2016 Sep;25(17-18):2579-89. doi: 10.1111/jocn.13301. Epub 2016 Aug 8. J Clin Nurs. 2016. PMID: 27501160 Clinical Trial.
-
Intensive lifestyle intervention improves cardiometabolic and exercise parameters in metabolically healthy obese and metabolically unhealthy obese individuals.Can J Cardiol. 2014 Apr;30(4):434-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2013.11.033. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Can J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24561010
-
Probiotic Foods and Supplements Interventions for Metabolic Syndromes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Recent Clinical Trials.Ann Nutr Metab. 2019;74(3):224-241. doi: 10.1159/000499028. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Ann Nutr Metab. 2019. PMID: 30889572
Cited by
-
Workplace-Based Education Interventions for Managing Metabolic Syndrome in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Realist Review.Public Health Chall. 2024 Jul 23;3(3):e224. doi: 10.1002/puh2.224. eCollection 2024 Sep. Public Health Chall. 2024. PMID: 40496523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medical Nutrition Therapy Provided by Dietitians is Effective and Saves Healthcare Costs in the Management of Adults with Dyslipidemia.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2023 Jun;25(6):331-342. doi: 10.1007/s11883-023-01096-0. Epub 2023 May 11. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2023. PMID: 37165278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 2005;112(17):2735–52. - PubMed
-
- Teramoto T, Sasaki J, Ueshima H, et al. Metabolic syndrome. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2008;15(1):1–5. - PubMed
-
- Zimmet P, Magliano D, Matsuzawa Y, Alberti G, Shaw J. The metabolic syndrome: a global public health problem and a new definition. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2005;12(6):295–300. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T, Tsubono Y, Kameda-Takemura K, et al. Magnitude of sustained multiple risk factors for ischemic heart disease in Japanese employees: a case-control study. Jpn Circ J. 2001;65(1):11–7. - PubMed
-
- Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease; pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(5):968–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

