The KUPNetViz: a biological network viewer for multiple -omics datasets in kidney diseases
- PMID: 23883183
- PMCID: PMC3725151
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-235
The KUPNetViz: a biological network viewer for multiple -omics datasets in kidney diseases
Abstract
Background: Constant technological advances have allowed scientists in biology to migrate from conventional single-omics to multi-omics experimental approaches, challenging bioinformatics to bridge this multi-tiered information. Ongoing research in renal biology is no exception. The results of large-scale and/or high throughput experiments, presenting a wealth of information on kidney disease are scattered across the web. To tackle this problem, we recently presented the KUPKB, a multi-omics data repository for renal diseases.
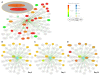
Results: In this article, we describe KUPNetViz, a biological graph exploration tool allowing the exploration of KUPKB data through the visualization of biomolecule interactions. KUPNetViz enables the integration of multi-layered experimental data over different species, renal locations and renal diseases to protein-protein interaction networks and allows association with biological functions, biochemical pathways and other functional elements such as miRNAs. KUPNetViz focuses on the simplicity of its usage and the clarity of resulting networks by reducing and/or automating advanced functionalities present in other biological network visualization packages. In addition, it allows the extrapolation of biomolecule interactions across different species, leading to the formulations of new plausible hypotheses, adequate experiment design and to the suggestion of novel biological mechanisms. We demonstrate the value of KUPNetViz by two usage examples: the integration of calreticulin as a key player in a larger interaction network in renal graft rejection and the novel observation of the strong association of interleukin-6 with polycystic kidney disease.
Conclusions: The KUPNetViz is an interactive and flexible biological network visualization and exploration tool. It provides renal biologists with biological network snapshots of the complex integrated data of the KUPKB allowing the formulation of new hypotheses in a user friendly manner.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

