Glatiramer acetate-induced acute hepatotoxicity in an adolescent with MS
- PMID: 23884038
- PMCID: PMC3908464
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182a2cc4a
Glatiramer acetate-induced acute hepatotoxicity in an adolescent with MS
Abstract
Glatiramer acetate (GA), a synthetic copolymer, is a frequently used first-line treatment for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Probable autoimmune hepatotoxicity during GA treatment has been reported,(1-4) but GA hepatotoxicity in the absence of positive autoimmune markers has not previously been described. Here, we report GA-induced hepatotoxicity in a pediatric patient with multiple sclerosis (MS).
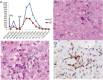
Figures
Comment in
-
Glatiramer acetate-induced acute hepatotoxicity in an adolescent with MS.Neurology. 2014 May 20;82(20):1846-7. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000450224.37865.80. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24843037 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Glatiramer acetate-induced acute hepatotoxicity in an adolescent with MS.Neurology. 2014 May 20;82(20):1846-7. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000450224.37865.80. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24843037 No abstract available.
-
Glatiramer acetate-induced hepatitis in a young female patient with multiple sclerosis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2014 Nov;3(6):732-4. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2014.08.001. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2014. PMID: 25891553
-
Glatiramer acetate induced hepatotoxicity.Curr Drug Saf. 2012 Apr;7(2):186-8. doi: 10.2174/157488612802715690. Curr Drug Saf. 2012. PMID: 22873505
-
Glatiramer acetate: a review of its use in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.CNS Drugs. 2002;16(12):825-50. doi: 10.2165/00023210-200216120-00004. CNS Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12421116 Review.
-
Spotlight on glatiramer acetate in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.BioDrugs. 2003;17(3):207-10. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200317030-00007. BioDrugs. 2003. PMID: 12749757 Review.
Cited by
-
Liver injury and glatiramer acetate, an uncommon association: case report and literature review.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2017 Nov;10(11):367-372. doi: 10.1177/1756285617722352. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2017. PMID: 29090021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing the initial choice and timing of therapy in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2015 Sep;8(5):212-32. doi: 10.1177/1756285615598910. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2015. PMID: 26557897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Disease-Modifying Therapies of Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis and Liver Injury: A Narrative Review.CNS Drugs. 2021 Aug;35(8):861-880. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00842-9. Epub 2021 Jul 28. CNS Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34319570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-induced liver injury by glatiramer acetate leading to liver transplant: A case report.JGH Open. 2023 Jul 26;7(8):591-593. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12938. eCollection 2023 Aug. JGH Open. 2023. PMID: 37649866 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Drug Selection in Children with Multiple Sclerosis: What Do We Know and What Remains Unanswered?Paediatr Drugs. 2025 Mar;27(2):161-179. doi: 10.1007/s40272-024-00675-1. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Paediatr Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39724509 Review.
References
-
- Neumann H, Csepregi A, Sailer M, Malfertheiner P. Glatiramer acetate induced acute exacerbation of autoimmune hepatitis in a patient with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 2007;254:816–817 - PubMed
-
- Pulicken M, Koteish A, DeBusk K, Calabresi PA. Unmasking of autoimmune hepatitis in a patient with MS following interferon beta therapy. Neurology 2006;66:1954–1955 - PubMed
-
- Subramaniam K, Pavli P, Llewellyn H, Chitturi S. Glatiramer acetate induced hepatotoxicity. Curr Drug Saf 2012;7:186–188 - PubMed
-
- Frese A, Bethke F, Ludemann P, Stogbauer F. Development of myasthenia gravis in a patient with multiple sclerosis during treatment with glatiramer acetate. J Neurol 2000;247:713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
