Bladder filling and voiding affect umbrella cell tight junction organization and function
- PMID: 23884145
- PMCID: PMC3798726
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00282.2013
Bladder filling and voiding affect umbrella cell tight junction organization and function
Abstract
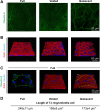
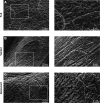
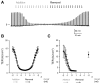
Epithelial cells are continuously exposed to mechanical forces including shear stress and stretch, although the effect these forces have on tight junction (TJ) organization and function are poorly understood. Umbrella cells form the outermost layer of the stratified uroepithelium and undergo large cell shape and surface area changes during the bladder cycle. Here we investigated the effects of bladder filling and voiding on the umbrella cell TJ. We found that bladder filling promoted a significant increase in the length of the TJ ring, which was quickly reversed within 5 min of voiding. Interestingly, when isolated uroepithelial tissue was mounted in Ussing chambers and exposed to physiological stretch, we observed a 10-fold drop in both transepithelial electrical resistance (TER) and the umbrella cell junctional resistance. The effects of stretch on TER were reversible and dependent on the applied force. Furthermore, the integrity of the umbrella cell TJ was maintained in the stretched uroepithelium, as suggested by the limited permeability of biotin, fluorescein, and ruthenium red. Finally, we found that depletion of extracellular Ca(2+) by EGTA completely disrupted the TER of unstretched, but not of stretched uroepithelium. Taken together, our studies indicate that the umbrella cell TJ undergoes major structural and functional reorganization during the bladder cycle. The impact of these changes on bladder function is discussed.
Keywords: bladder; claudins; stretch; tight junction; uroepithelium.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Stretch-regulated exocytosis/endocytosis in bladder umbrella cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Mar;13(3):830-46. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-09-0435. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11907265 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine receptor expression and function in bladder uroepithelium.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 Aug;291(2):C254-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00025.2006. Epub 2006 Mar 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16571869
-
Uropathogenic E. coli promote a paracellular urothelial barrier defect characterized by altered tight junction integrity, epithelial cell sloughing and cytokine release.J Comp Pathol. 2012 Jul;147(1):11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Oct 19. J Comp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22014415 Free PMC article.
-
Cell biology and physiology of the uroepithelium.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):F1477-501. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00327.2009. Epub 2009 Jul 8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19587142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The uroepithelium: not just a passive barrier.Traffic. 2004 Mar;5(3):117-28. doi: 10.1046/j.1600-0854.2003.00156.x. Traffic. 2004. PMID: 15086788 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary K+ promotes irritative voiding symptoms and pain in the face of urothelial barrier dysfunction.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 2;9(1):5509. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41971-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30940909 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder infection with uropathogenic Escherichia coli increases the excitability of afferent neurons.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Jan 1;322(1):F1-F13. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00167.2021. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34779263 Free PMC article.
-
Periostin Attenuates Cyclophosphamide-induced Bladder Injury by Promoting Urothelial Stem Cell Proliferation and Macrophage Polarization.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022 Jun 22;11(6):659-673. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szac025. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35648087 Free PMC article.
-
3D printed biaxial stretcher compatible with live fluorescence microscopy.HardwareX. 2020 Apr;7:e00095. doi: 10.1016/j.ohx.2020.e00095. Epub 2020 Feb 5. HardwareX. 2020. PMID: 35097243 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Adaptation and Autophagic Competence Shape Response to Fluid Shear Stress in T24 Bladder Cancer Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 3;12:647350. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.647350. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34012396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya P, Beckel J, Ruiz WG, Wang E, Rojas R, Birder L, Apodaca G. Distribution of the tight junction proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-4, -8, and -12 in bladder epithelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287: F305–F318, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Apodaca G. Stretch-regulated exocytosis of discoidal vesicles in urinary bladder epithelium. Urology 57: 103–104, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bruewer M, Utech M, Ivanov AI, Hopkins AM, Parkos CA, Nusrat A. Interferon-gamma induces internalization of epithelial tight junction proteins via a macropinocytosis-like process. FASEB J 19: 923–933, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Cavanaugh KJ, Jr, Margulies SS. Measurement of stretch-induced loss of alveolar epithelial barrier integrity with a novel in vitro method. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283: C1801–C1808, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

