The size, burden and cost of disorders of the brain in the UK
- PMID: 23884863
- PMCID: PMC3778981
- DOI: 10.1177/0269881113495118
The size, burden and cost of disorders of the brain in the UK
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this paper is to increase awareness of the prevalence and cost of psychiatric and neurological disorders (brain disorders) in the UK.
Method: UK data for 18 brain disorders were extracted from a systematic review of European epidemiological data and prevalence rates and the costs of each disorder were summarized (2010 values).
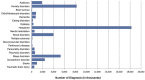
Results: There were approximately 45 million cases of brain disorders in the UK, with a cost of €134 billion per annum. The most prevalent were headache, anxiety disorders, sleep disorders, mood disorders and somatoform disorders. However, the five most costly disorders (€ million) were: dementia: €22,164; psychotic disorders: €16,717; mood disorders: €19,238; addiction: €11,719; anxiety disorders: €11,687. Apart from psychosis, these five disorders ranked amongst those with the lowest direct medical expenditure per subject (<€3000). The approximate breakdown of costs was: 50% indirect costs, 25% direct non-medical and 25% direct healthcare costs.
Discussion: The prevalence and cost of UK brain disorders is likely to increase given the ageing population. Translational neurosciences research has the potential to develop more effective treatments but is underfunded. Addressing the clinical and economic challenges posed by brain disorders requires a coordinated effort at an EU and national level to transform the current scientific, healthcare and educational agenda.
Keywords: Brain disorders; burden; cost.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Fineberg has consulted for Lundbeck, Glaxo-Smith Kline, Transcept, Novartis and Servier.
Dr Fineberg has received research support from Lundbeck, Glaxo-SmithKline, Wellcome, Cephalon, European College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ECNP), Servier, UK Medical Research Council, UK National Institute of Health Research.
Dr Fineberg has received honoraria for lectures at scientific meetings from Janssen, Lundbeck, Servier, Astra Zeneca, Wyeth, Bristol Myers Squibb.
Dr Fineberg has received financial support to attend scientific meetings from Lundbeck, Servier, Bristol Myers Squibb, International College of Obsessive Compulsive Spectrum Disorders, British Association for Psychopharmacology, International Conference on Behavioral Addictions, ECNP, World Health Organization.
In the last 3 years PMH has received support to attend conferences and/or fees for lecturing and consultancy work (including attending advisory boards) from Astra-Zeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Servier and Sunovion.
Barbara Sahakian consults for Cambridge Cognition, Servier and Lundbeck. She holds a grant from Janssen/J&J.
In the last 2 years I have consulted for Lundbeck, Pfizer, GSK, Rekitts, BMS, Lilly and Otsuka.
Figures
References
-
- AccessEconomics (2007) The cost of muscular dystrophy. Muscular Dystrophy Association. AccessEconomics.
-
- Alzheimer’s Society (2007) A report to the Alzheimer’s Society on the prevalence and economic cost of dementia in the UK produced by King’s College London and London School of Economics. London: Dementia UK.
-
- Andlin-Sobocki P, Bengt Jönsson P, Wittchen HU. (2005) Cost of disorders of the brain in Europe. Eur J Neurol 12: 1–27. - PubMed
-
- APA (American Psychiatric Association) (1980) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- APA (American Psychiatric Association) (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (3rd ed., revised). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical