Ex vivo generation of highly purified and activated natural killer cells from human peripheral blood
- PMID: 23885718
- PMCID: PMC3753730
- DOI: 10.1089/hgtb.2012.183
Ex vivo generation of highly purified and activated natural killer cells from human peripheral blood
Abstract
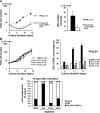
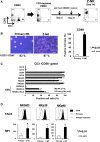
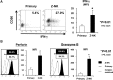
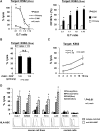
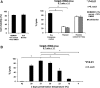
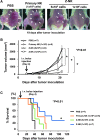
Adoptive immunotherapy using natural killer (NK) cells has been a promising treatment for intractable malignancies; however, there remain a number of difficulties with respect to the shortage and limited anticancer potency of the effector cells. We here established a simple feeder-free method to generate purified (>90%) and highly activated NK cells from human peripheral blood-derived mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Among the several parameters, we found that CD3 depletion, high-dose interleukin (IL)-2, and use of a specific culture medium were sufficient to obtain highly purified, expanded (∼200-fold) and activated CD3(-)/CD56(+) NK cells from PBMCs, which we designated zenithal-NK (Z-NK) cells. Almost all Z-NK cells expressed the lymphocyte-activated marker CD69 and showed dramatically high expression of activation receptors (i.e., NKG2D), interferon-γ, perforin, and granzyme B. Importantly, only 2 hours of reaction at an effector/target ratio of 1:1 was sufficient to kill almost all K562 cells, and the antitumor activity was also replicated in tumor-bearing mice in vivo. Cytolysis was specific for various tumor cells, but not for normal cells, irrespective of MHC class I expression. These findings strongly indicate that Z-NK cells are purified, expanded, and near-fully activated human NK cells and warrant further investigation in a clinical setting.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of natural killer and natural killer-like T cells derived from ex vivo expanded and activated cord blood mononuclear cells: implications for adoptive cellular immunotherapy.Exp Hematol. 2009 Oct;37(10):1216-29. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2009.07.009. Epub 2009 Jul 26. Exp Hematol. 2009. PMID: 19638292
-
The potential markers of NK-92 associated to cytotoxicity against K562 cells.Biologicals. 2020 Nov;68:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2020.08.009. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Biologicals. 2020. PMID: 32933840
-
Optimization of Human NK Cell Manufacturing: Fully Automated Separation, Improved Ex Vivo Expansion Using IL-21 with Autologous Feeder Cells, and Generation of Anti-CD123-CAR-Expressing Effector Cells.Hum Gene Ther. 2017 Oct;28(10):897-913. doi: 10.1089/hum.2017.157. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Hum Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 28810809
-
Characterization of cord blood natural killer and lymphokine activated killer lymphocytes following ex vivo cellular engineering.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006 Jun;12(6):608-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.01.009. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006. PMID: 16737934
-
Cytokine-induced killer cells are terminally differentiated activated CD8 cytotoxic T-EMRA lymphocytes.Exp Hematol. 2009 May;37(5):616-628.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2009.01.010. Exp Hematol. 2009. PMID: 19375652
Cited by
-
Engineered NK Cells Against Cancer and Their Potential Applications Beyond.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 15;13:825979. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.825979. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35242135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy for colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Dec 14;19(46):8531-42. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i46.8531. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24379570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contemporary Approaches to Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jun 19;16(12):2270. doi: 10.3390/cancers16122270. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in NK cell production.Cell Mol Immunol. 2022 Apr;19(4):460-481. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00808-3. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34983953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aparicio-Pagés M.N. Verspaget H.W. Peña A.S. Lamers C.B. Natural killer cell activity in patients with adenocarcinoma in the upper gastrointestinal tract. J. Clin. Lab. Immunol. 1991;35:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Arai S. Meagher R. Swearingen M., et al. Infusion of the allogeneic cell line NK-92 in patients with advanced renal cell cancer or melanoma: a phase I trial. Cytotherapy. 2008;10:625–632. - PubMed
-
- Berg M. Childs R. Ex-vivo expansion of NK cells: What is the priority - high yield or high purity? Cytotherapy. 2010;12:969–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

