Post-radioembolization yttrium-90 PET/CT - part 2: dose-response and tumor predictive dosimetry for resin microspheres
- PMID: 23885971
- PMCID: PMC3733999
- DOI: 10.1186/2191-219X-3-57
Post-radioembolization yttrium-90 PET/CT - part 2: dose-response and tumor predictive dosimetry for resin microspheres
Abstract
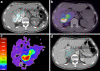
Background: Coincidence imaging of low-abundance yttrium-90 (90Y) internal pair production by positron emission tomography with integrated computed tomography (PET/CT) achieves high-resolution imaging of post-radioembolization microsphere biodistribution. Part 2 analyzes tumor and non-target tissue dose-response by 90Y PET quantification and evaluates the accuracy of tumor 99mTc macroaggregated albumin (MAA) single-photon emission computed tomography with integrated CT (SPECT/CT) predictive dosimetry.
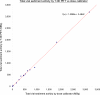
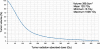
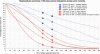
Methods: Retrospective dose quantification of 90Y resin microspheres was performed on the same 23-patient data set in part 1. Phantom studies were performed to assure quantitative accuracy of our time-of-flight lutetium-yttrium-oxyorthosilicate system. Dose-responses were analyzed using 90Y dose-volume histograms (DVHs) by PET voxel dosimetry or mean absorbed doses by Medical Internal Radiation Dose macrodosimetry, correlated to follow-up imaging or clinical findings. Intended tumor mean doses by predictive dosimetry were compared to doses by 90Y PET.
Results: Phantom studies demonstrated near-perfect detector linearity and high tumor quantitative accuracy. For hepatocellular carcinomas, complete responses were generally achieved at D70 > 100 Gy (D70, minimum dose to 70% tumor volume), whereas incomplete responses were generally at D70 < 100 Gy; smaller tumors (<80 cm3) achieved D70 > 100 Gy more easily than larger tumors. There was complete response in a cholangiocarcinoma at D70 90 Gy and partial response in an adrenal gastrointestinal stromal tumor metastasis at D70 53 Gy. In two patients, a mean dose of 18 Gy to the stomach was asymptomatic, 49 Gy caused gastritis, 65 Gy caused ulceration, and 53 Gy caused duodenitis. In one patient, a bilateral kidney mean dose of 9 Gy (V20 8%) did not cause clinically relevant nephrotoxicity. Under near-ideal dosimetric conditions, there was excellent correlation between intended tumor mean doses by predictive dosimetry and those by 90Y PET, with a low median relative error of +3.8% (95% confidence interval, -1.2% to +13.2%).
Conclusions: Tumor and non-target tissue absorbed dose quantification by 90Y PET is accurate and yields radiobiologically meaningful dose-response information to guide adjuvant or mitigative action. Tumor 99mTc MAA SPECT/CT predictive dosimetry is feasible. 90Y DVHs may guide future techniques in predictive dosimetry.
Figures


References
-
- Kao YH, Steinberg JD, Tay YS, Lim GKY, Yan J, Townsend DW, Takano A, Burgmans MC, Irani FG, Teo TKB, Yeow TN, Gogna A, Lo RHG, Tay KH, Tan BS, Chow PKH, Satchithanantham S, Tan AEH, Ng DCE, Goh ASW. Post-radioembolization yttrium-90 PET/CT - part 1: diagnostic reporting. EJNMMI Res. 2013;3:56. doi: 10.1186/2191-219X-3-56. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Salem R, Lewandowski RJ, Gates VL, Nutting CW, Murthy R, Rose SC, Soulen MC, Geschwind JF, Kulik L, Kim YH, Spreafico C, Maccauro M, Bester L, Brown DB, Ryu RK, Sze DY, Rilling WS, Sato KT, Sangro B, Bilbao JI, Jakobs TF, Ezziddin S, Kulkarni S, Kulkarni A, Liu DM, Valenti D, Hilgard P, Antoch G, Muller SP, Alsuhaibani H. et al.Research reporting standards for radioembolization of hepatic malignancies. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;3:265–278. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2010.10.029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

