Ibrutinib is an irreversible molecular inhibitor of ITK driving a Th1-selective pressure in T lymphocytes
- PMID: 23886836
- PMCID: PMC3795457
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-06-507947
Ibrutinib is an irreversible molecular inhibitor of ITK driving a Th1-selective pressure in T lymphocytes
Abstract
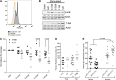
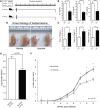
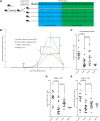
Given its critical role in T-cell signaling, interleukin-2-inducible kinase (ITK) is an appealing therapeutic target that can contribute to the pathogenesis of certain infectious, autoimmune, and neoplastic diseases. Ablation of ITK subverts Th2 immunity, thereby potentiating Th1-based immune responses. While small-molecule ITK inhibitors have been identified, none have demonstrated clinical utility. Ibrutinib is a confirmed irreversible inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) with outstanding clinical activity and tolerability in B-cell malignancies. Significant homology between BTK and ITK alongside in silico docking studies support ibrutinib as an immunomodulatory inhibitor of both ITK and BTK. Our comprehensive molecular and phenotypic analysis confirms ITK as an irreversible T-cell target of ibrutinib. Using ibrutinib clinical trial samples along with well-characterized neoplastic (chronic lymphocytic leukemia), parasitic infection (Leishmania major), and infectious disease (Listeria monocytogenes) models, we establish ibrutinib as a clinically relevant and physiologically potent ITK inhibitor with broad therapeutic utility. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01105247 and #NCT01217749.
Figures



Comment in
-
Two targets for the price of one.Blood. 2013 Oct 10;122(15):2529-31. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-518548. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24113792 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dubovsky JA, Villagra A, Powers JJ, Wang HW, Pinilla-Ibarz J, Sotomayor EM. Circumventing immune tolerance through epigenetic modification. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(3):268–276. - PubMed
-
- Loose D, Van de Wiele C. The immune system and cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2009;24(3):369–376. - PubMed
-
- Berg LJ, Finkelstein LD, Lucas JA, Schwartzberg PL. Tec family kinases in T lymphocyte development and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:549–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

