Periodicities designed in the tropomyosin sequence and structure define its functions
- PMID: 23887197
- PMCID: PMC3782539
- DOI: 10.4161/bioa.25616
Periodicities designed in the tropomyosin sequence and structure define its functions
Abstract
Tropomyosin is an actin binding protein that regulates actin filament dynamics and its interactions with actin binding proteins such as myosin, tropomodulin, formin, Arp2/3 and ADF-cofilin in most eukaryotic cells. Tropomyosin is the prototypical two-chained, α-helical coiled coil protein that associates end-to-end and binds to both sides of the actin filament. Each tropomyosin molecule spans four to seven actin monomers in the filament, depending on the size of the tropomyosin. Tropomyosins have a periodic heptad repeat sequence that is characteristic of coiled coil proteins as well as additional periodicities required for its interaction with the actin filament, where each periodic repeat interacts with one actin molecule. This review addresses the role of periodic features of the Tm molecule in carrying out its universal functions of binding to the actin filament and its regulation and the specific features that may determine the isoform specificity of tropomyosins.
Keywords: actin filament; coiled coil; cytoskeleton; muscle regulation; tropomyosin.
Figures

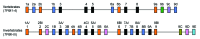

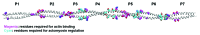
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
