Thrombocytopenia induced by the histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat involves p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms
- PMID: 23887629
- PMCID: PMC3730430
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.260
Thrombocytopenia induced by the histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat involves p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms
Abstract
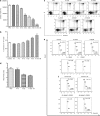
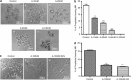
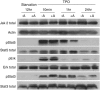
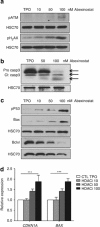
Abexinostat is a pan histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi) that demonstrates efficacy in malignancy treatment. Like other HDACi, this drug induces a profound thrombocytopenia whose mechanism is only partially understood. We have analyzed its effect at doses reached in patient plasma on in vitro megakaryopoiesis derived from human CD34(+) cells. When added at day 0 in culture, abexinostat inhibited CFU-MK growth, megakaryocyte (MK) proliferation and differentiation. These effects required only a short incubation period. Decreased proliferation was due to induction of apoptosis and was not related to a defect in TPO/MPL/JAK2/STAT signaling. When added later (day 8), the compound induced a dose-dependent decrease (up to 10-fold) in proplatelet (PPT) formation. Gene profiling from MK revealed a silencing in the expression of DNA repair genes with a marked RAD51 decrease at protein level. DNA double-strand breaks were increased as attested by elevated γH2AX phosphorylation level. Moreover, ATM was phosphorylated leading to p53 stabilization and increased BAX and p21 expression. The use of a p53 shRNA rescued apoptosis, and only partially the defect in PPT formation. These results suggest that HDACi induces a thrombocytopenia by a p53-dependent mechanism along MK differentiation and a p53-dependent and -independent mechanism for PPT formation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phase 1 study of oral abexinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in combination with doxorubicin in patients with metastatic sarcoma.Cancer. 2015 Apr 15;121(8):1223-30. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29175. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25536954 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling-based optimisation of administration schedule for the histone deacetylase inhibitor abexinostat (S78454/PCI-24781) in phase I.Eur J Cancer. 2013 Sep;49(13):2791-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23790467 Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase I/II Multicenter, Open-Label Study of the Oral Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Abexinostat in Relapsed/Refractory Lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Mar 1;22(5):1059-66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0624. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26482040 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic modeling of abexinostat-induced thrombocytopenia across different patient populations: application for the determination of the maximum tolerated doses in both lymphoma and solid tumour patients.Invest New Drugs. 2014 Oct;32(5):985-94. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0118-1. Epub 2014 May 31. Invest New Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24875134 Clinical Trial.
-
p53 at the Crossroads between Different Types of HDAC Inhibitor-Mediated Cancer Cell Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 15;20(10):2415. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102415. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31096697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an UPLC-MS/MS method for quantitative analysis of abexinostat levels in rat plasma and application of pharmacokinetics.BMC Chem. 2024 Feb 20;18(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01144-z. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 38378603 Free PMC article.
-
First-in-human study of the toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of CG200745, a pan-HDAC inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid malignancies.Invest New Drugs. 2015 Oct;33(5):1048-57. doi: 10.1007/s10637-015-0262-2. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Invest New Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26076682 Clinical Trial.
-
ETV6 germline mutations cause HDAC3/NCOR2 mislocalization and upregulation of interferon response genes.JCI Insight. 2020 Sep 17;5(18):e140332. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.140332. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32841218 Free PMC article.
-
Romiplostim in chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia: A review of the literature.Cancer Med. 2024 Aug;13(15):e7429. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7429. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39135303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application and investigation of thrombopoiesis-stimulating agents in the treatment of thrombocytopenia.Ther Adv Hematol. 2023 Feb 27;14:20406207231152746. doi: 10.1177/20406207231152746. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Hematol. 2023. PMID: 36865986 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boyes J, Byfield P, Nakatani Y, Ogryzko V. Regulation of activity of the transcription factor GATA-1 by acetylation. Nature. 1998;396:594–598. - PubMed
-
- Gu W, Roeder RG. Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by acetylation of the p53 C-terminal domain. Cell. 1997;90:595–606. - PubMed
-
- Janke C, Bulinski JC. Post-translational regulation of the microtubule cytoskeleton: mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:773–786. - PubMed
-
- Minucci S, Pelicci PG. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:38–51. - PubMed
-
- Yang XJ, Seto E. HATs and HDACs: from structure, function and regulation to novel strategies for therapy and prevention. Oncogene. 2007;26:5310–5318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

