Sirolimus-FKBP12.6 impairs endothelial barrier function through protein kinase C-α activation and disruption of the p120-vascular endothelial cadherin interaction
- PMID: 23887639
- PMCID: PMC3827918
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301659
Sirolimus-FKBP12.6 impairs endothelial barrier function through protein kinase C-α activation and disruption of the p120-vascular endothelial cadherin interaction
Abstract
Objective: Sirolimus (SRL) is an immunosuppressant drug used to prevent rejection in organ transplantation and neointimal hyperplasia when delivered from drug-eluting stents. Major side effects of SRL include edema and local collection of intimal lipid deposits at drug-eluting stent sites, suggesting that SRL impairs endothelial barrier function (EBF). The aim of this study was to address the role of SRL on impaired EBF and the potential mechanisms involved.
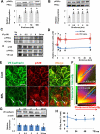
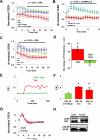
Approach and results: Cultured human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) and intact human and mouse endothelium was examined to determine the effect of SRL, which binds FKBP12.6 to inhibit the mammalian target of rapamycin, on EBF. EBF, measured by transendothelial electrical resistance, was impaired in HAECs when treated with SRL or small interfering RNA for FKBP12.6 and reversed when pretreated with ryanodine, a stabilizer of ryanodine receptor 2 intracellular calcium release channels. Intracellular calcium increased in HAECs treated with SRL and normalized with ryanodine pretreatment. SRL-treated HAECs demonstrated increases in protein kinase C-α phosphorylation, a calcium sensitive serine/threonine kinase important in vascular endothelial (VE) cadherin barrier function through its interaction with p120-catenin (p120). Immunostaining of HAECs, human coronary and mouse aortic endothelium treated with SRL showed disruption of p120-VE cadherin interaction treated with SRL. SRL impairment of HAEC EBF was reduced with protein kinase C-α small interfering RNA. Mice treated with SRL demonstrated increased vascular permeability by Evans blue albumin extravasation in the lungs, heart, and aorta.
Conclusions: SRL-FKBP12.6 impairs EBF by activation of protein kinase C-α and downstream disruption of the p120-VE cadherin interaction in vascular endothelium. These data suggest this mechanism may be an important contributor of SRL side effects related to impaired EBF.
Keywords: PKC; endothelium; sirolimus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PKCα activation of p120-catenin serine 879 phospho-switch disassembles VE-cadherin junctions and disrupts vascular integrity.Circ Res. 2012 Aug 31;111(6):739-49. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.269654. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22798526 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Targeting of the mTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin) Kinase Improves Endothelial Permeability in Drug-Eluting Stents-Brief Report.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Sep;38(9):2217-2224. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311321. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30026269
-
Differential regulation of endothelial cell permeability by high and low doses of oxidized 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Mar;46(3):331-41. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0153OC. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21997484 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Regulation of Vascular Permeability by Vascular Endothelial Cadherin-Mediated Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions.J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(4):148-159. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.148. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017. PMID: 28978894 Review.
-
Cross talk between focal adhesion kinase and cadherins: role in regulating endothelial barrier function.Microvasc Res. 2012 Jan;83(1):3-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2011.08.001. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Microvasc Res. 2012. PMID: 21864544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Sirolimus and Magnesium on Primary Human Coronary Endothelial Cells: An In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2930. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032930. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769252 Free PMC article.
-
A TEMPOL and rapamycin loaded nanofiber-covered stent favors endothelialization and mitigates neointimal hyperplasia and local inflammation.Bioact Mater. 2022 May 11;19:666-677. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.04.033. eCollection 2023 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 35600979 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic alterations in coronary cell lines exposed to sirolimus and paclitaxel.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jun 6. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04101-4. Online ahead of print. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40481235
-
Everolimus-eluting stents improve vascular response in a diabetic animal model.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014 Aug;7(4):526-32. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.113.001023. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014. PMID: 24915972 Free PMC article.
-
Everolimus-induced hyperpermeability of endothelial cells causes lung injury.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Dec;248(23):2440-2448. doi: 10.1177/15353702231220672. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 38158699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Vermeer MA, Negre-Aminou P, Lankelma J, Emeis JJ, van Hinsbergh VW. Simvastatin improves disturbed endothelial barrier function. Circulation. 2000;102:2803–2809. - PubMed
-
- Mehta D, Malik AB. Signaling mechanisms regulating endothelial permeability. Physiological reviews. 2006;86:279–367. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Vilchez F, Vazquez de Prada JA, Almenar L, et al. Withdrawal of proliferation signal inhibitors due to adverse events in the maintenance phase of heart transplantation. The Journal of heart and lung transplantation : the official publication of the International Society for Heart Transplantation. 2012;31:288–295. - PubMed
-
- Park SJ, Kang SJ, Virmani R, Nakano M, Ueda Y. In-stent neoatherosclerosis: A final common pathway of late stent failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2012;59:2051–2057. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

