Exposure to environmental toxicants and pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: state of the art and research perspectives
- PMID: 23887652
- PMCID: PMC3759860
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140815286
Exposure to environmental toxicants and pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: state of the art and research perspectives
Abstract
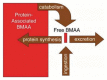
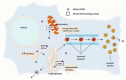
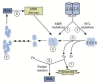
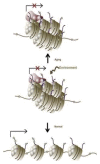
There is a broad scientific consensus that amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a fatal neuromuscular disease, is caused by gene--environment interactions. In fact, given that only about 10% of all ALS diagnosis has a genetic basis, gene-environmental interaction may give account for the remaining percentage of cases. However, relatively little attention has been paid to environmental and lifestyle factors that may trigger the cascade of motor neuron degeneration leading to ALS, although exposure to chemicals--including lead and pesticides-agricultural environments, smoking, intense physical activity, trauma and electromagnetic fields have been associated with an increased risk of ALS. This review provides an overview of our current knowledge of potential toxic etiologies of ALS with emphasis on the role of cyanobacteria, heavy metals and pesticides as potential risk factors for developing ALS. We will summarize the most recent evidence from epidemiological studies and experimental findings from animal and cellular models, revealing that potential causal links between environmental toxicants and ALS pathogenesis have not been fully ascertained, thus justifying the need for further research.
Figures
References
-
- Kiernan M.C., Vucic S., Cheah B.C., Turner M.R., Eisen A., Hardiman O., Burrell J.R., Zoing M.C. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet. 2011;6736:61156–61157. - PubMed
-
- Ludolph A.C., Brettschneider J., Weishaupt J.H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2012;25:530–535. - PubMed
-
- Rosen D.R., Siddique T., Patterson D., Figlewicz D.A., Sapp P., Hentati A., Donaldson D., Goto J., O’Regan J.P., Deng H.X., et al. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature. 1993;362:59–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

