Treating anxiety after stroke using cognitive-behaviour therapy: two cases
- PMID: 23889561
- PMCID: PMC3856474
- DOI: 10.1080/09602011.2013.820135
Treating anxiety after stroke using cognitive-behaviour therapy: two cases
Abstract
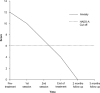
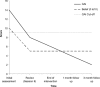
Anxiety disorders are common after stroke. However, information on how to treat them with psychotherapy in this population is highly limited. Modified cognitive-behaviour therapy (CBT) has the potential to assist. Two cases of individuals treated with modified CBT for anxiety after stroke are presented. The modification was required in light of deficits in executive and memory function in one individual and in the context of communication difficulties in the other. The anxiety symptoms were treated over seven and nine sessions, respectively. Both participants improved following the intervention, and these improvements were maintained at 3 month follow-ups. Further case-series and randomised controlled designs are required to support and develop modified CBT for those with anxiety after stroke.
Figures
References
-
- Aström M. Generalised anxiety disorder in stroke patients. Stroke. 1996;27:270–276. - PubMed
-
- Arundine A. M., Bradbury C. L. P., Dupuis K. M. A., Dawson D. R. P., Ruttan L. A. P., Green R. E. A. P. Cognitive behaviour therapy after acquired brain injury: Maintenance of therapeutic benefits at 6 months post treatment. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation. 2012;27:104–112. - PubMed
-
- Ayers C. R., Sorrell J. T., Thorp S. R., Wetherell J. L. Evidence-based psychological treatments for late-life anxiety. Psychology & Ageing. 2007;22(1):8–17. - PubMed
-
- Broomfield N. M., Laidlaw K., Hickabottom E., Murray M. F., Pendrey R., Whittick J. E., Gillespie D. C. Post-stroke depression: The case for augmented, individually tailored cognitive behavioural therapy. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy. 2010;18:202–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
