Increasing pregnancy-related use of prescribed opioid analgesics
- PMID: 23889859
- PMCID: PMC3888316
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2013.05.017
Increasing pregnancy-related use of prescribed opioid analgesics
Abstract
Purpose: To quantify the prevalence of prescribed opioid analgesics among pregnant women enrolled in Tennessee Medicaid from 1995 to 2009.
Methods: Retrospective cohort study of 277,555 pregnancies identified from birth and fetal death certificates, and linked to previously validated, computerized pharmacy records. Poisson regression was used to estimate trends over time, rate ratios, and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
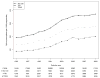
Results: During the study period, 29% of pregnant women filled a prescription for an opioid analgesic. From 1995 to 2009, any pregnancy-related use increased 1.90-fold (95% CI, 1.83-1.98), first trimester use increased 2.27-fold (95% CI, 2.14-2.41), and second or third trimester use increased 2.02-fold (95% CI, 1.93-2.12), after adjusting for maternal characteristics. Any pregnancy-related, first trimester, and second or third trimester use were each more likely among mothers who were at least 21 years old, white, non-Hispanic, prima gravid, resided in nonurban areas, enrolled in Medicaid owing to disability, and who had less than a high school education.
Conclusions: Opioid analgesic use by Tennessee Medicaid-insured pregnant women increased nearly 2-fold from 1995 to 2009. Additional study is warranted to understand the implications of this increased use.
Keywords: Opioids; Pregnancy; Prescription.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zerzan JT, Morden NE, Soumerai S, Ross-Degnan D, Roughead E, Zhang F, et al. Trends and geographic variation of opiate medication use in state Medicaid fee-for-service programs, 1996 to 2002. Med Care. 2006;44(11):1005–10. - PubMed
-
- Becker WC, Sullivan LE, Tetrault JM, Desai RA, Fiellin DA. Non-medical use, abuse and dependence on prescription opioids among U.S. adults: psychiatric, medical and substance use correlates. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008;94(1–3):38–47. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum HG, White AG, Reynolds JL, Greenberg PE, Zhang M, Vallow S, et al. Estimated costs of prescription opioid analgesic abuse in the United States in 2001: a societal perspective. Clin J Pain. 2006;22(8):667–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

