Clinical features and sera anti-aquaporin 4 antibody positivity in patients with demyelinating disorders of the central nervous system from Tianjin, China
- PMID: 23890015
- PMCID: PMC6492993
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12156
Clinical features and sera anti-aquaporin 4 antibody positivity in patients with demyelinating disorders of the central nervous system from Tianjin, China
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the clinical characteristics and sera anti-aquaporin 4 (AQP4) antibody positivity in patients with inflammatory demyelinating disorders (IDDs) of the central nervous system (CNS) in Tianjin, China.
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 234 patients with IDDs including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), recurrent optic neuritis (rON), longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM), clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), and multiple sclerosis (MS) groups. Sera from 217 patients were determined for AQP4-Ab. The clinical characteristics and sera anti-AQP4 positivity were compared.
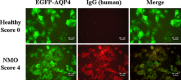
Results: The IDDS comprised 63 MS, 51 NMO, 56 LETM, 10 rON, and 54 CIS. Compared with MS, NMO had a higher frequency of occurrence in women, intractable hiccup and nausea (IHN), medullospinal lesion, longitudinally extensive spinal cord lesions (LESCL) and bilateral ON, disease onset at a later age, and worsening residual disability. AQP4-Ab-positive rates were 84.1% and 69% in NMO and NMO spectrum disorders (NMOSD), respectively, whereas it was undetectable in all of the MS sera samples.
Conclusions: We comprehensively contrast the distinct clinical features of MS, NMO, and NMOSD in our center. A sensitive AQP4-Ab assay is necessary for the early diagnosis of NMOSD in our patients. Neither medullospinal lesion nor IHN is unique in NMO.
Keywords: Anti-aquaporin 4 antibody; Chinese; Clinical features; Multiple sclerosis; Neuromyelitis optica.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Misu T, Fujihara K, Nakashima I, Sato S, Itoyama Y. Intractable hiccup and nausea with periaqueductal lesions in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 2005;65:1479–1482. - PubMed
-
- Kira J. Multiple sclerosis in the Japanese population. Lancet Neurol 2003;2:117–127. - PubMed
-
- Osoegawa M, Kira J, Fukazawa T, et al. Temporal changes and geographical differences in multiple sclerosis phenotypes in Japanese: Nationwide survey results over 30 years. Mult Scler 2009;15:159–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

