BRL37344, a β3-adrenergic receptor agonist, decreases nerve-evoked contractions in human detrusor smooth muscle isolated strips: role of BK channels
- PMID: 23890664
- PMCID: PMC3758792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.05.027
BRL37344, a β3-adrenergic receptor agonist, decreases nerve-evoked contractions in human detrusor smooth muscle isolated strips: role of BK channels
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the mechanism by which BRL37344, a β3-adrenergic receptor (β3-ARs) agonist, facilitates the inhibition of nerve-evoked contractions in human detrusor smooth muscle (DSM) isolated strips and to identify the role of large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK) channels in this process.
Methods: Human DSM specimens were obtained from open bladder surgeries on patients without preoperative history of overactive bladder symptoms. Isometric DSM tension recordings were conducted using force-displacement transducers and thermostatically controlled tissue baths. Nerve-evoked contractions were generated by electrical field stimulation (EFS).
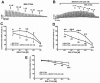
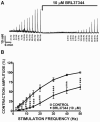
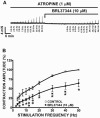
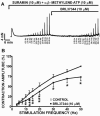
Results: BRL37344, a β3-AR agonist, significantly decreased the amplitude, muscle force, and duration of the DSM contractions induced by 20 Hz EFS, in a concentration-dependent manner. This BRL37344-mediated inhibition of the amplitude and muscle force of the nerve-evoked DSM contraction was significantly reduced by iberiotoxin, a highly selective inhibitor of the BK channel, revealing a role for BK channels in the β3-AR-induced inhibition of human DSM nerve-evoked contractions. We further used atropine, α,β-methylene-ATP, and suramin to separate the cholinergic and purinergic components of human DSM nerve-evoked contractions. We found that the β3-AR agonist, BRL37344, inhibited both components of the EFS-induced (0.5-50 Hz) DSM contractions.
Conclusion: This study supports the concept that β3-AR agonists inhibit nerve-evoked contractions in human DSM. We have further revealed that BK channels play a critical role in BRL37344-mediated relaxation of nerve-evoked contractions in human DSM. The study suggests that in addition to β3-ARs, BK channels may also represent promising pharmacologic targets in the treatment of urinary bladder dysfunction.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Biers SM, Reynard JM, Brading AF. The effects of a new selective beta3-adrenoceptor agonist (GW427353) on spontaneous activity and detrusor relaxation in human bladder. BJU Int. 2006;98(6):1310–4. - PubMed
-
- Igawa Y, Schneider T, Yamazaki Y, et al. Functional investigation of beta-adrenoceptors in human isolated detrusor focusing on the novel selective beta3-adrenoceptor agonist KUC-7322. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012;385(8):759–67. - PubMed
-
- Tyagi P, Thomas CA, Yoshimura N, Chancellor MB. Investigations into the presence of functional Beta1, Beta2 and Beta3-adrenoceptors in urothelium and detrusor of human bladder. Int Braz J Urol. 2009;35(1):76–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

