Sex hormones and risk of breast cancer in premenopausal women: a collaborative reanalysis of individual participant data from seven prospective studies
- PMID: 23890780
- PMCID: PMC4056766
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70301-2
Sex hormones and risk of breast cancer in premenopausal women: a collaborative reanalysis of individual participant data from seven prospective studies
Abstract
Background: Associations between circulating concentrations of oestrogens, progesterone, and androgens with breast cancer and related risk factors in premenopausal women are not well understood. We aimed to characterise these associations with a pooled analysis of data from seven studies.
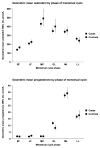
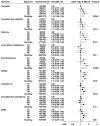
Methods: Individual participant data for prediagnostic sex hormone and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) concentrations were contributed from seven prospective studies. We restricted analyses to women who were premenopausal and younger than 50 years at blood collection, and to women with breast cancer diagnosed before age 50 years. We estimated odds ratios (ORs) with 95% CIs for breast cancer associated with hormone concentrations by conditional logistic regression in cases and controls matched for age, date of blood collection, and day of cycle, with stratification by study and further adjustment for cycle phase. We examined associations of hormones with risk factors for breast cancer in control women by comparing geometric mean hormone concentrations in categories of these risk factors, adjusted for study, age, phase of menstrual cycle, and body-mass index (BMI). All statistical tests were two-sided.
Findings: We included data for up to 767 women with breast cancer and 1699 controls in the risk analyses. Breast cancer risk was associated with a doubling in concentrations of oestradiol (OR 1·19, 95% CI 1·06-1·35), calculated free oestradiol (1·17, 1·03-1·33), oestrone (1·27, 1·05-1·54), androstenedione (1·30, 1·10-1·55), dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (1·17, 1·04-1·32), testosterone (1·18, 1·03-1·35), and calculated free testosterone (1·08, 0·97-1·21). Breast cancer risk was not associated with luteal phase progesterone (doubling in concentration OR 1·00, 95% CI 0·92-1·09), and adjustment for other factors had little effect on any of these ORs. Cross-sectional analyses in control women showed several associations of sex hormones with breast cancer risk factors.
Interpretation: Circulating oestrogens and androgens are positively associated with the risk for breast cancer in premenopausal women.
Copyright © 2013 Endogenous Hormones and Breast Cancer Collaborative Group. Open Access article distributed under the terms of CC BY. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All members of the writing committee declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- MacMahon B, Cole P, Brown J. Etiology of human breast cancer: a review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;50:21–42. - PubMed
-
- Endogenous Hormones and Breast Cancer Collaborative Group. Endogenous sex hormones and breast cancer in postmenopausal women: reanalysis of nine prospective studies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:606–16. - PubMed
-
- Kaaks R, Rinaldi S, Key TJ, et al. Postmenopausal serum androgens, oestrogens and breast cancer risk: the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:1071–82. - PubMed
-
- Helzlsouer KJ, Gordon GB, Alberg AJ, Bush TL, Comstock GW. Relationship of prediagnostic serum levels of dehydroepiandrosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate to the risk of developing premenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992;52:1–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

