Type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 23890997
- PMCID: PMC4380133
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60591-7
Type 1 diabetes
Abstract
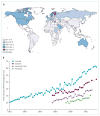
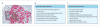
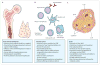
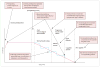
Over the past decade, knowledge of the pathogenesis and natural history of type 1 diabetes has grown substantially, particularly with regard to disease prediction and heterogeneity, pancreatic pathology, and epidemiology. Technological improvements in insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors help patients with type 1 diabetes manage the challenge of lifelong insulin administration. Agents that show promise for averting debilitating disease-associated complications have also been identified. However, despite broad organisational, intellectual, and fiscal investments, no means for preventing or curing type 1 diabetes exists, and, globally, the quality of diabetes management remains uneven. This Seminar discusses current progress in epidemiology, pathology, diagnosis, and treatment of type 1 diabetes, and prospects for an improved future for individuals with this disease.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Todd JA. Etiology of type 1 diabetes. Immunity. 2010;32:457–67. - PubMed
-
- Gale EA. Type 1 diabetes in the young: the harvest of sorrow goes on. Diabetologia. 2005;48:1435–38. - PubMed
-
- Harjutsalo V, Sjoberg L, Tuomilehto J. Time trends in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children: a cohort study. Lancet. 2008;371:1777–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

