ZMYND10 is mutated in primary ciliary dyskinesia and interacts with LRRC6
- PMID: 23891469
- PMCID: PMC3738827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.06.007
ZMYND10 is mutated in primary ciliary dyskinesia and interacts with LRRC6
Abstract
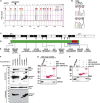
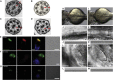
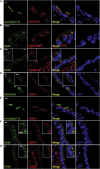
Defects of motile cilia cause primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), characterized by recurrent respiratory infections and male infertility. Using whole-exome resequencing and high-throughput mutation analysis, we identified recessive biallelic mutations in ZMYND10 in 14 families and mutations in the recently identified LRRC6 in 13 families. We show that ZMYND10 and LRRC6 interact and that certain ZMYND10 and LRRC6 mutations abrogate the interaction between the LRRC6 CS domain and the ZMYND10 C-terminal domain. Additionally, ZMYND10 and LRRC6 colocalize with the centriole markers SAS6 and PCM1. Mutations in ZMYND10 result in the absence of the axonemal protein components DNAH5 and DNALI1 from respiratory cilia. Animal models support the association between ZMYND10 and human PCD, given that zmynd10 knockdown in zebrafish caused ciliary paralysis leading to cystic kidneys and otolith defects and that knockdown in Xenopus interfered with ciliogenesis. Our findings suggest that a cytoplasmic protein complex containing ZMYND10 and LRRC6 is necessary for motile ciliary function.
Copyright © 2013 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Noone P.G., Leigh M.W., Sannuti A., Minnix S.L., Carson J.L., Hazucha M., Zariwala M.A., Knowles M.R. Primary ciliary dyskinesia: diagnostic and phenotypic features. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004;169:459–467. - PubMed
-
- Zariwala M.A., Knowles M.R., Omran H. Genetic defects in ciliary structure and function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007;69:423–450. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy M.P., Omran H., Leigh M.W., Dell S., Morgan L., Molina P.L., Robinson B.V., Minnix S.L., Olbrich H., Severin T. Congenital heart disease and other heterotaxic defects in a large cohort of patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Circulation. 2007;115:2814–2821. - PubMed
-
- Schwabe G.C., Hoffmann K., Loges N.T., Birker D., Rossier C., de Santi M.M., Olbrich H., Fliegauf M., Failly M., Liebers U. Primary ciliary dyskinesia associated with normal axoneme ultrastructure is caused by DNAH11 mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2008;29:289–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK092808-01A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U54 HL096458-06/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK068306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092808/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK091405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- EY013408/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK053093/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000083/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL175156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013408/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK070263/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK091405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- DK070263/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5 R01HL071798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY000331/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HL096458/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK090917/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053093/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 DK090917/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM089970/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR019480/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK091405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

