FGF14 localization and organization of the axon initial segment
- PMID: 23891806
- PMCID: PMC3791165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.07.008
FGF14 localization and organization of the axon initial segment
Abstract
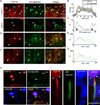
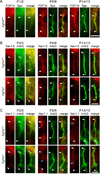
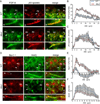
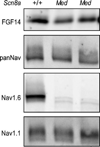
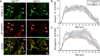
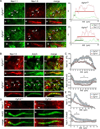
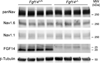
The axon initial segment (AIS) is highly enriched in the structural proteins ankyrin G and βIV-spectrin, the pore-forming (α) subunits of voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channels, and functional Nav channels, and is critical for the initiation of action potentials. We previously reported that FGF14, a member of the intracellular FGF (iFGF) sub-family, is expressed in cerebellar Purkinje neurons and that the targeted inactivation of Fgf14 in mice (Fgf14(-/-)) results in markedly reduced Purkinje neuron excitability. Here, we demonstrate that FGF14 immunoreactivity is high in the AIS of Purkinje neurons and is distributed in a decreasing, proximal to distal, gradient. This pattern is evident early in the postnatal development of Purkinje neurons and is also observed in many other types of central neurons. In (Scn8a(med)) mice, which are deficient in expression of the Nav1.6 α subunit, FGF14 immunoreactivity is markedly increased and expanded in the Purkinje neuron AIS, in parallel with increased expression of the Nav1.1 (Scn1a) α subunit and expanded expression of βIV-spectrin. Although Nav1.1, FGF14, and βIV-spectrin are affected, ankyrin G immunoreactivity at the AIS of Scn8a(med) and wild type (WT) Purkinje neurons was not significantly different. In Fgf14(-/-) Purkinje neurons, βIV-spectrin and ankyrin G immunoreactivity at the AIS were also similar to WT Purkinje neurons, although both the Nav1.1 and Nav1.6 α subunits are modestly, but significantly (p<0.005), reduced within sub-domains of the AIS, changes that may contribute to the reduced excitability of Fgf14(-/-) Purkinje neurons.
Keywords: AIS; Ankyrin G; Axon initial segment; FGF14; Nav; Purkinje neuron; Scn1a; Scn8a; Voltage-gated sodium channel; axon initial segment; fibroblast growth factor 14; iFGF; intracellular fibroblast growth factor; voltage gated sodium channel; βIV-spectrin.
© 2013.
Figures
References
-
- Ango F, di Cristo G, Higashiyama H, Bennett V, Wu P, Huang ZJ. Ankyrin-Based Subcellular Gradient of Neurofascin, an Immunoglobulin Family Protein, Directs GABAergic Innervation at Purkinje Axon Initial Segment. Cell. 2004;119:257–272. - PubMed
-
- Brusse E, de Koning I, Maat-Kievit A, Oostra BA, Heutink P, van Swieten JC. Spinocerebellar ataxia associated with a mutation in the fibroblast growth factor 14 gene (SCA27): A new phenotype. Mov. Disord. 2006;21:396–401. - PubMed
-
- Burgess DL, Kohrman DC, Galt J, Plummer NW, Jones JM, Spear B, Meisler MH. Mutation of a new sodium channel gene, Scn8a, in the mouse mutant ‘motor endplate disease’. Nat. Genet. 1995;10:461–465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

