Exposure to inhaled particulate matter activates early markers of oxidative stress, inflammation and unfolded protein response in rat striatum
- PMID: 23892126
- PMCID: PMC4318358
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.07.012
Exposure to inhaled particulate matter activates early markers of oxidative stress, inflammation and unfolded protein response in rat striatum
Abstract
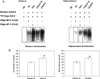
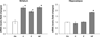
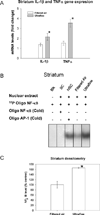
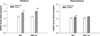
To study central nervous system airborne PM related subchronic toxicity, SD male rats were exposed for eight weeks to either coarse (32 μg/m³), fine (178 μg/m³) or ultrafine (107 μg/m³) concentrated PM or filtered air. Different brain regions (olfactory bulb, frontal cortex, striatum and hippocampus), were harvested from the rats following exposure to airborne PM. Subsequently, prooxidant (HO-1 and SOD-2), and inflammatory markers (IL-1β and TNFα), apoptotic (caspase 3), and unfolded protein response (UPR) markers (XBP-1S and BiP), were also measured using real-time PCR. Activation of nuclear transcription factors Nrf-2 and NF-κB, associated with antioxidant and inflammation processes, respectively, were also analyzed by GSMA. Ultrafine PM increased HO-1 and SOD-2 mRNA levels in the striatum and hippocampus, in the presence of Nrf-2 activation. Also, ultrafine PM activated NF-κB and increased IL-1β and TNFα in the striatum. Activation of UPR was observed after exposure to coarse PM through the increment of XBP-1S and BiP in the striatum, accompanied by an increase in antioxidant response markers HO-1 and SOD-2. Our results indicate that exposure to different size fractions of PM may induce physiological changes (in a neuroanatomical manner) in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically within the striatum, where inflammation, oxidative stress and UPR signals were effectively activated.
Keywords: ATF6; BiP; Central nervous system; GSMA; HO-1; IL-1β; IRE1α; Inflammation; NF-κB; Nrf-2; Oxidative stress; PAHs; PERK; PM; Particulate matter; SOD; Striatum; TNFα; UPR; Unfolded protein response; VACES; X-box binding protein 1; XBP-1; XBP-1 spliced form; XBP-1 unspliced form; XBP-1S; XBP-1U; activating transcription factor 6; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha kinase 3; gel shift mobility assay; heat shock 70kDa protein 5 (glucose-regulated protein, 78kDa); heme oxygenase 1; inositol-requiring protein 1; interleukin 1 beta; nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; particulate matter; polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons; superoxide dismutase; tumor necrosis factor-alpha; unfolded protein response; versatile aerosol concentrator system.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Abbott A. Dementia: a problem for our age. Nature. 2011;475:S2–S4. - PubMed
-
- Bandopadhyay R, de Belleroche J. Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: emerging role of molecular chaperones. Trends in Molecular Medicine. 2010;16:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Block ML, Wu X, Pei Z, Li G, Wang T, Qin L, Wilson B, Yang J, Hong JS, Veronesi B. Nanometer size diesel exhaust particles are selectively toxic to dopaminergic neurons: the role of microglia, phagocytosis, and NADPH oxidase. FASEB Journal. 2004;18:1618–1620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

