Neurotoxicity of methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine
- PMID: 23892199
- PMCID: PMC3870191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.07.014
Neurotoxicity of methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine
Abstract
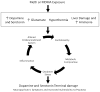
Amphetamines are a class of psychostimulant drugs that are widely abused for their stimulant, euphoric, empathogenic and hallucinogenic properties. Many of these effects result from acute increases in dopamine and serotonin neurotransmission. Subsequent to these acute effects, methamphetamine and 3,4 methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) produce persistent damage to dopamine and serotonin nerve terminals. This review summarizes the numerous interdependent mechanisms including excitotoxicity, mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress that have been demonstrated to contribute to this damage. Emerging non-neuronal mechanisms by which the drugs may contribute to monoaminergic terminal damage, as well as the neuropsychiatric consequences of this terminal damage are also presented. Methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) have similar chemical structures and pharmacologic properties compared to other abused substances including cathinone (khat), as well as a relatively new class of novel synthetic amphetamines known as 'bath salts' that have gained popularity among drug abusers.
Keywords: 3-4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine; Excitotoxicity; Methamphetamine; Neurotoxicity; Oxidative stress; Psychosis.
© 2013.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest:
All authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures
References
-
- Ago M, Ago K, Hara K, Kashimura S, Ogata M. Toxicological and histopathological analysis of a patient who died nine days after a single intravenous dose of methamphetamine: a case report. Leg Med (Tokyo) 2006;8:235–239. - PubMed
-
- Anneken JH, Cunningham JI, Collins SA, Yamamoto BK, Gudelsky GA. MDMA increases glutamate release and reduces parvalbumin-positive GABAergic cells in the dorsal hippocampus of the rat: role of cyclooxygenase. Journal of neuroimmune pharmacology : the official journal of the Society on NeuroImmune Pharmacology. 2013;8:58–65. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arai S, Takuma K, Mizoguchi H, Ibi D, Nagai T, Takahashi K, Kamei H, Nabeshima T, Yamada K. Involvement of pallidotegmental neurons in methamphetamine- and MK-801-induced impairment of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex in mice: reversal by GABAB receptor agonist baclofen. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:3164–3175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

