Inflammatory responses in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
- PMID: 23892271
- PMCID: PMC3764334
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2013.89
Inflammatory responses in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
Abstract
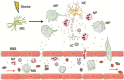
Inflammation plays a critical role in mediating brain injury induced by neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). The mechanisms underlying inflammatory responses to ischemia may be shared by neonatal and adult brains; however, HIE exhibits a unique inflammation phenotype that results from the immaturity of the neonatal immune system. This review will discuss the current knowledge concerning systemic and local inflammatory responses in the acute and subacute stages of HIE. The key components of inflammation, including immune cells, adhesion molecules, cytokines, chemokines and oxidative stress, will be reviewed, and the differences between neonatal and adult inflammatory responses to cerebral ischemic injury will also be discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Vannucci RC, Perlman JM. Interventions for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 1997;100:1004–14. - PubMed
-
- Gluckman PD, Williams CE. When and why do brain cells die. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1992;34:1010–4. - PubMed
-
- Lorek A, Takei Y, Cady EB, Wyatt JS, Penrice J, Edwards AD, et al. Delayed (“secondary”) cerebral energy failure after acute hypoxia-ischemia in the newborn piglet: continuous 48-hour studies by phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1994;36:699–706. - PubMed
-
- Penrice J, Cady EB, Lorek A, Wylezinska M, Amess PN, Aldridge RF, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain in normal preterm and term infants, and early changes after perinatal hypoxia-ischemia. Pediatr Res. 1996;40:6–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

