Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs
- PMID: 23892355
- PMCID: PMC3859717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.022
Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs
Abstract
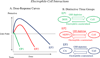
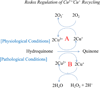
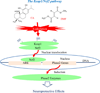
Living cells maintain a balance between oxidation and reduction, and perturbations of this redox balance are thought to contribute to various diseases. Recent attempts to regulate redox state have focused on electrophiles (EPs), which activate potent cellular defense systems against oxidative stress. One example of this approach is exemplified by carnosic acid (CA) and carnosol (CS), compounds that are found in the herb rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis). Importantly, CA and CS themselves are not electrophilic, but in response to oxidation, become electrophilic, and then activate the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE (antioxidant-response element) transcription pathway to synthesize endogenous antioxidant "phase 2" enzymes. As a result of our efforts to develop these compounds as therapeutics for brain health, we have formulated two innovative criteria for drug development: the first concept is the use of pro-electrophilic drugs (PEDs) that are innocuous in and of themselves; and the second concept involves the use of compounds that are pathologically activated therapeutics (PATs);i.e., these small molecules are chemically converted to their active form by the very oxidative stress that they are designed to then combat. The chemical basis for PED and PAT drugs is embodied in the ortho- and para-hydroquinone electrophilic cores of the molecules, which are oxidized by the Cu(2+)/Cu(+) cycling system (or potentially by other transition metals). Importantly, this cycling pathway is under stringent regulation by the cell redox state. We propose that redox-dependent quinone formation is the predominant mechanism for formation of PED and PAT drugs from their precursor compounds. In fact, redox-dependent generation of the active form of drug from the "pro-form" distinguishes this therapeutic approach from traditional EPs such as curcumin, and results in a decrease in clinical side effects at therapeutic concentrations, e.g., lack of reaction with other thiols such as glutathione (GSH), which can result in lowering GSH and inducing oxidative stress in normal cells. We consider this pro-drug quality of PED/PAT compoundsto be a key factor for generating drugs to be used to combat neurodegenerative diseases that will be clinically tolerated. Given the contribution of oxidative stress to the pathology of multiple neurodegenerative diseases, the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway represents a promising drug target for these PED/PAT agents.
Keywords: ABCC; ARE; ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C; Antioxidant-response element; CA; CS; Carnosol; DA; DMF; DOX; Dimethyl fumarate (also known as BG-12); Dopamine; Doxorubicin (also known as adriamycin); EP; Electrophile; Electrophilic counterattack; GCLC; GCLM; GSH; GST; Glutamyl cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; Glutamyl cysteine ligase modifier subunit; Glutathione; Glutathione-S-transferase; H(2)O(2); HO-1; HSE; HSF-1; HSP; Heat-shock factor-1; Heat-shock protein; Hemeoxygenase-1; Hydrogen peroxide; Keap1; Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; MS; Multiplesclerosis; NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1; NEPP; NGF; NQO1; Na(+)-independent cystine-glutamate exchanger; Nerve growth factor; Neurite outgrowth-promoting prostaglandin; Nrf2; Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2; PAT; PD; PED; Parkinson's disease; Pathologically activated therapeutic; Pro-electrophilic drug; RNS; ROS; Reactive nitrogen species; Reactive oxygen species; STR; Strongylophorin; TBHQ; Tert-butylhydroquinone; carnosic acid; heat-responsive element; xCT.
© 2013 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


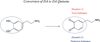




Republished in
-
Reprint of: Nrf2/ARE-mediated antioxidant actions of pro-electrophilic drugs.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jan;66:45-57. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24262357
References
-
- Talalay P. Chemoprotection against cancer by induction of phase 2 enzymes. Biofactors. 2000;12:5–11. - PubMed
-
- Hayes JD, McMahon M, Chowdhry S, Dinkova-Kostova AT. Cancer chemoprevention mechanisms mediated through the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010;13:1713–1748. - PubMed
-
- Itoh K, Tong KI, Yamamoto M. Molecular mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive response to electrophiles. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2004;36:1208–1213. - PubMed
-
- Taguchi K, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M. Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in stress response and cancer evolution. Genes Cells. 2011;16:123–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

