A new strategy for gene targeting and functional proteomics using the DT40 cell line
- PMID: 23892402
- PMCID: PMC3783193
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt650
A new strategy for gene targeting and functional proteomics using the DT40 cell line
Abstract
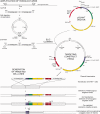
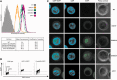
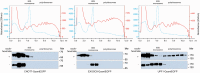
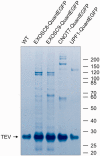
DT40 cells derived from chicken B lymphocytes exhibit exceptionally high homologous recombination rates. Therefore, they can be used as a convenient tool and model for gene targeting experiments. However, lack of efficient cloning strategies, protein purification protocols and a well annotated protein database limits the utility of these cells for proteomic studies. Here we describe a fast and inexpensive experimental pipeline for protein localization, quantification and mass spectrometry-based interaction studies using DT40 cells. Our newly designed set of pQuant vectors and a sequence- and ligation-independent cloning (SLIC) strategy allow for simple and efficient generation of gene targeting constructs, facilitating homologous-recombination-based protein tagging on a multi-gene scale. We also report proof of principle results using the key proteins involved in RNA decay, namely EXOSC8, EXOSC9, CNOT7 and UPF1.
Figures


References
-
- Gavin AC, Bosche M, Krause R, Grandi P, Marzioch M, Bauer A, Schultz J, Rick JM, Michon AM, Cruciat CM, et al. Functional organization of the yeast proteome by systematic analysis of protein complexes. Nature. 2002;415:141–147. - PubMed
-
- Ho Y, Gruhler A, Heilbut A, Bader GD, Moore L, Adams SL, Millar A, Taylor P, Bennett K, Boutilier K, et al. Systematic identification of protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mass spectrometry. Nature. 2002;415:180–183. - PubMed
-
- Gavin AC, Aloy P, Grandi P, Krause R, Boesche M, Marzioch M, Rau C, Jensen LJ, Bastuck S, Dumpelfeld B, et al. Proteome survey reveals modularity of the yeast cell machinery. Nature. 2006;440:631–636. - PubMed
-
- Huh WK, Falvo JV, Gerke LC, Carroll AS, Howson RW, Weissman JS, O'Shea EK. Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature. 2003;425:686–691. - PubMed
-
- Krogan NJ, Cagney G, Yu H, Zhong G, Guo X, Ignatchenko A, Li J, Pu S, Datta N, Tikuisis AP, et al. Global landscape of protein complexes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 2006;440:637–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

