Doxorubicin induces atypical NF-κB activation through c-Abl kinase activity in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23892407
- PMCID: PMC11824581
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-013-1476-3
Doxorubicin induces atypical NF-κB activation through c-Abl kinase activity in breast cancer cells
Abstract
Purpose: NF-κB transcription factor has been associated with cancer development and chemoresistance. We studied the signaling pathway activated by doxorubicin (DOX) leading to NF-κB activation in breast cancer cells.
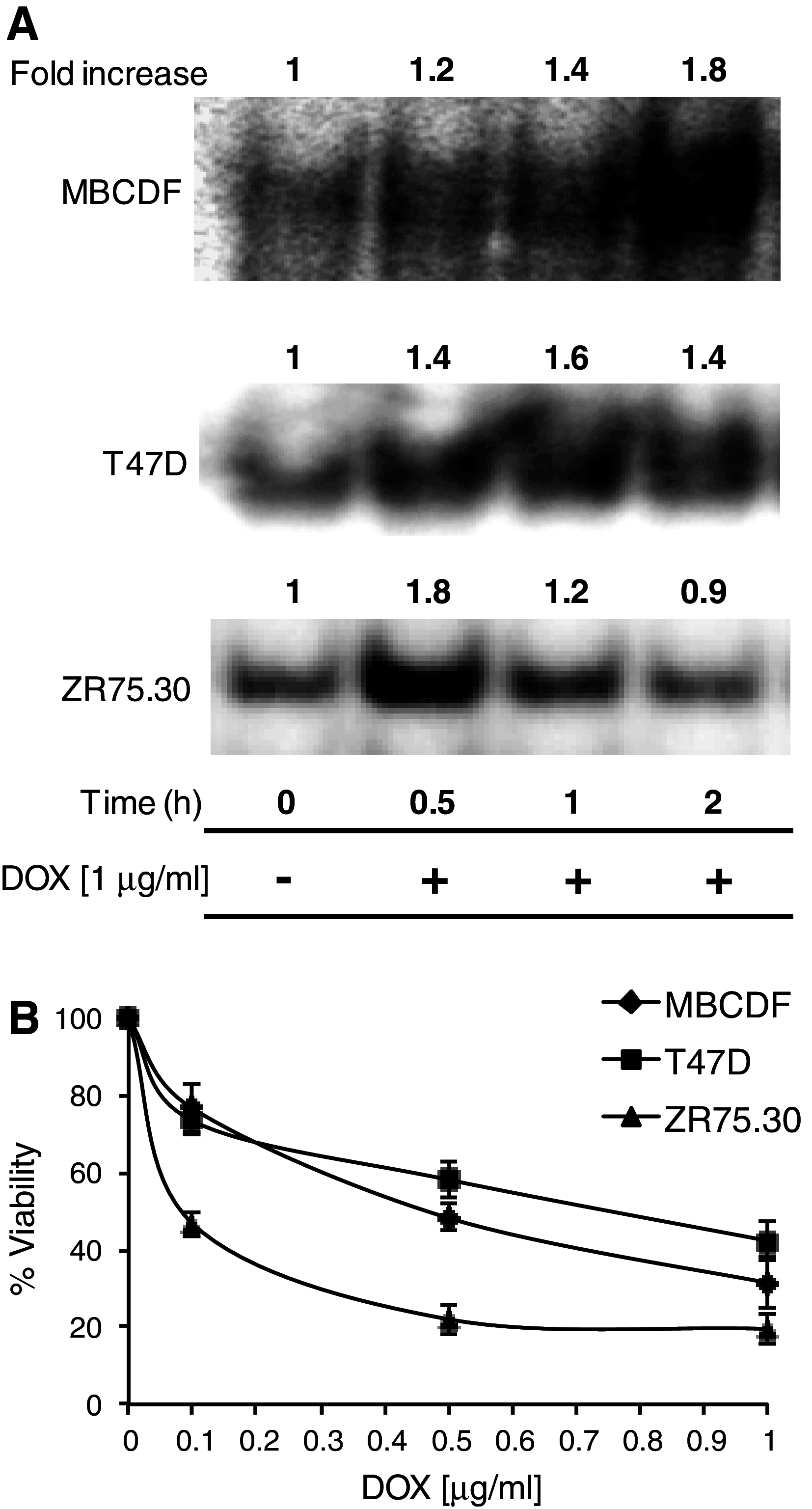
Methods: NF-κB activity was evaluated by electrophoretic mobility shift in T47D, ZR75.30 and primary culture (MBCDF) from a ductal infiltrating carcinoma. Cell viability was measured by crystal violet. Western blotting was performed to check the expression and phosphorylation of IκBα Ser-32/36. c-Abl was inhibited with Imatinib or by overexpressing a dominant negative form of c-Abl (K290R).
Results: We found a correlation between sensitivity to DOX and amplitude of NF-κB activation. In cells least sensitive to DOX, NF-κB remained activated for longer time (T47D and MBCDF). The opposite effect was observed in cells sensitive to DOX (ZR75.30). DOX did not induce IκBα degradation or Ser-32/36 phosphorylation. Instead, there were modifications in the levels of IκBα tyrosine phosphorylation, suggesting an atypical NF-κB activation. In DOX-resistant cells, Imatinib treatment reduced IκBα tyrosine phosphorylation and NF-κB activity. The Imatinib-DOX combination significantly enhanced cell death of T47D and MBCDF breast cancer cells. Overexpression of c-Abl K290R in T47D and MBCDF cells reduced basal and DOX-induced NF-κB activation as well as IκBα tyrosine phosphorylation. In c-Abl K290R cells, DOX treatment did not mimic the combination Imatinib-DOX-induced cell death.
Conclusions: Inhibition of c-Abl inactivated IκBα/NF-κB pathway is associated with IκBα tyrosine phosphorylation in breast cancer cells. These results also raise the potential use of a combined therapy with Imatinib and DOX for breast cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enhanced ABL-inhibitor-induced MAPK-activation in T315I-BCR-ABL-expressing cells: a potential mechanism of altered leukemogenicity.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 Feb;138(2):203-12. doi: 10.1007/s00432-011-1086-x. Epub 2011 Nov 17. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22089930 Free PMC article.
-
Imatinib reverses doxorubicin resistance by affecting activation of STAT3-dependent NF-κB and HSP27/p38/AKT pathways and by inhibiting ABCB1.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055509. Epub 2013 Jan 31. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383209 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasomal Degradation of TRAF2 Mediates Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Doxorubicin-Cardiomyopathy.Circulation. 2022 Sep 20;146(12):934-954. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.058411. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35983756 Free PMC article.
-
Dasatinib and nilotinib for imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic myeloid leukaemia: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(22):1-410. doi: 10.3310/hta16220. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 22551803 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of imatinib for first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia in chronic phase: a systematic review and economic analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2004 Jul;8(28):iii, 1-120. doi: 10.3310/hta8280. Health Technol Assess. 2004. PMID: 15245690
Cited by
-
IL-17A Increases Doxorubicin Efficacy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 18;12:928474. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.928474. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35924165 Free PMC article.
-
Second-generation proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib enhances doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):73697-73710. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12048. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27655642 Free PMC article.
-
The Abl1 tyrosine kinase is a key player in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy and its p53/p73 cell death mediated signaling differs in atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes.J Transl Med. 2024 Sep 16;22(1):845. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05623-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39285385 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation proteasome inhibitor oprozomib enhances sensitivity to doxorubicin in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 May 1;11(5):2347-2355. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938346 Free PMC article.
-
A Practical Review of Proteasome Pharmacology.Pharmacol Rev. 2019 Apr;71(2):170-197. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.015370. Pharmacol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30867233 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basseres DS, Baldwin AS (2006) Nuclear factor-κB and inhibitor of κB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene 25(51):6817–6830 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

