Mining large-scale response networks reveals 'topmost activities' in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- PMID: 23892477
- PMCID: PMC3725478
- DOI: 10.1038/srep02302
Mining large-scale response networks reveals 'topmost activities' in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
Abstract
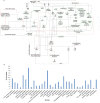
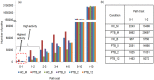
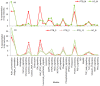
Mycobacterium tuberculosis owes its high pathogenic potential to its ability to evade host immune responses and thrive inside the macrophage. The outcome of infection is largely determined by the cellular response comprising a multitude of molecular events. The complexity and inter-relatedness in the processes makes it essential to adopt systems approaches to study them. In this work, we construct a comprehensive network of infection-related processes in a human macrophage comprising 1888 proteins and 14,016 interactions. We then compute response networks based on available gene expression profiles corresponding to states of health, disease and drug treatment. We use a novel formulation for mining response networks that has led to identifying highest activities in the cell. Highest activity paths provide mechanistic insights into pathogenesis and response to treatment. The approach used here serves as a generic framework for mining dynamic changes in genome-scale protein interaction networks.
Figures




References
-
- WHO. Report No. WHO/HTM/TB/2012.6. (2012).
-
- Casadevall A. & Pirofski L-a. Host-Pathogen Interactions: The Attributes of Virulence. J. Infect Dis. 184, 337–344 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee S., Sambarey A., Prashanthi K. & Chandra N. Current trends in modeling host–pathogen interactions. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Knowl Discov. 3, 109–128 (2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

