Toll-6 and Toll-7 function as neurotrophin receptors in the Drosophila melanogaster CNS
- PMID: 23892553
- PMCID: PMC4634317
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3474
Toll-6 and Toll-7 function as neurotrophin receptors in the Drosophila melanogaster CNS
Abstract
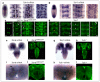
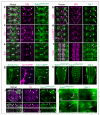
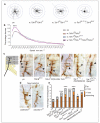
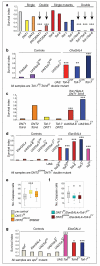
Neurotrophin receptors corresponding to vertebrate Trk, p75(NTR) or Sortilin have not been identified in Drosophila, thus it is unknown how neurotrophism may be implemented in insects. Two Drosophila neurotrophins, DNT1 and DNT2, have nervous system functions, but their receptors are unknown. The Toll receptor superfamily has ancient evolutionary origins and a universal function in innate immunity. Here we show that Toll paralogs unrelated to the mammalian neurotrophin receptors function as neurotrophin receptors in fruit flies. Toll-6 and Toll-7 are expressed in the CNS throughout development and regulate locomotion, motor axon targeting and neuronal survival. DNT1 (also known as NT1 and spz2) and DNT2 (also known as NT2 and spz5) interact genetically with Toll-6 and Toll-7, and DNT1 and DNT2 bind to Toll-6 and Toll-7 promiscuously and are distributed in vivo in domains complementary to or overlapping with those of Toll-6 and Toll-7. We conclude that in fruit flies, Tolls are not only involved in development and immunity but also in neurotrophism, revealing an unforeseen relationship between the neurotrophin and Toll protein families.
Figures


References
-
- Leulier F, Lemaitre B. Toll-like receptors--taking an evolutionary approach. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:165–178. doi:nrg2303 [pii]10.1038/nrg2303. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr., Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.083001.084359 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Imler JL, Zheng L. Biology of Toll receptors: lessons from insects and mammals. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;75:18–26. doi:10.1189/jlb.0403160 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell. 1996;86:973–983. doi:S0092-8674(00)80172-5 [pii] - PubMed
REFERENCE APPEARING ONLY IN METHODS
-
- Weber AN, Gangloff M, Moncrieffe MC, Hyvert Y, Imler JL, Gay NJ. Role of the Spatzle Pro-domain in the generation of an active toll receptor ligand. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:13522–13531. doi:M700068200 [pii] 10.1074/jbc.M700068200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

