An extracellular Serine/Threonine-rich protein from Lactobacillus plantarum NCIMB 8826 is a novel aggregation-promoting factor with affinity to mucin
- PMID: 23892754
- PMCID: PMC3811371
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01657-13
An extracellular Serine/Threonine-rich protein from Lactobacillus plantarum NCIMB 8826 is a novel aggregation-promoting factor with affinity to mucin
Abstract
Autoaggregation in lactic acid bacteria is directly related to the production of certain extracellular proteins, notably, aggregation-promoting factors (APFs). Production of aggregation-promoting factors confers beneficial traits to probiotic-producing strains, contributing to their fitness for the intestinal environment. Furthermore, coaggregation with pathogens has been proposed to be a beneficial mechanism in probiotic lactic acid bacteria. This mechanism would limit attachment of the pathogen to the gut mucosa, favoring its removal by the human immune system. In the present paper, we have characterized a novel aggregation-promoting factor in Lactobacillus plantarum. A mutant with a knockout of the D1 gene showed loss of its autoaggregative phenotype and a decreased ability to bind to mucin, indicating an adhesion role of this protein. In addition, heterologous production of the D1 protein or an internal fragment of the protein, characterized by its abundance in serine/threonine, strongly induced autoaggregation in Lactococcus lactis. This result strongly suggested that this internal fragment is responsible for the bioactivity of D1 as an APF. To our knowledge, this is the first report on a gene coding for an aggregation-promoting factor in Lb. plantarum.
Figures
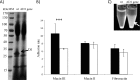
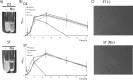
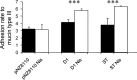
References
-
- Chevallier B, Hubert JC, Kammerer B. 1994. Determination of chromosome size and number of rrn loci in Lactobacillus plantarum by pulsed-field gel-electrophoresis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 120:51–56 - PubMed
-
- Kleerebezem M, Boekhorst J, van Kranenburg R, Molenaar D, Kuipers OP, Leer R, Tarchini R, Peters SA, Sandbrink HM, Fiers MW, Stiekema W, Lankhorst RMK, Bron PA, Hoffer SM, Groot MN, Kerkhoven R, de Vries M, Ursing B, de Vos WM, Siezen RJ. 2003. Complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100:1990–1995 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tallon R, Arias S, Bressollier P, Urdaci MC. 2007. Strain- and matrix-dependent adhesion of Lactobacillus plantarum is mediated by proteinaceous bacterial compounds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 102:442–451 - PubMed
-
- de Vries MC, Vaughan EE, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM. 2006. Lactobacillus plantarum—survival, functional and potential probiotic properties in the human intestinal tract. Int. Dairy J. 16:1018–1028
-
- Molin G. 2001. Probiotics in foods not containing milk or milk constituents, with special reference to Lactobacillus plantarum 299v. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 73:380S–385S - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

