Effect of baclofen on morphine-induced conditioned place preference, extinction, and stress-induced reinstatement in chronically stressed mice
- PMID: 23892776
- PMCID: PMC3889653
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-013-3204-8
Effect of baclofen on morphine-induced conditioned place preference, extinction, and stress-induced reinstatement in chronically stressed mice
Abstract
Rationale and objective: A stress-induced increase in excitability can result from a reduction in inhibitory neurotransmission. Modulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic transmission is an effective treatment for drug seeking and relapse. This study investigated whether baclofen, a GABA(B) receptor agonist, had an impact on morphine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP), extinction, and stress-induced relapse in chronically stressed mice.
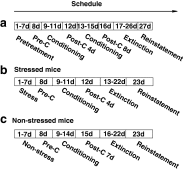
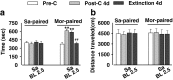
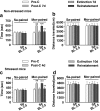
Methods: Chronic stress was induced by restraining mice for 2 h for seven consecutive days. We first investigated whether chronic stress influenced morphine-induced CPP, extinction, and stress-induced relapse in the stressed mice. Next, we investigated whether three different doses of baclofen influenced chronic stress as measured by the expression of morphine-induced CPP. We chose the most effective dose for subsequent extinction and reinstatement experiments. Reinstatement of morphine-induced CPP was induced by a 6-min forced swim stress. Locomotor activity was also measured for each test.
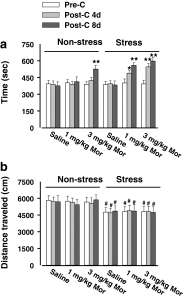
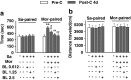
Results: Chronic stress facilitated the expression of morphine-induced CPP and prolonged extinction time. Forced swim stress primed the reinstatement of morphine-induced CPP in mice. Baclofen treatment affected the impact of chronic stress on different phases of morphine-induced CPP.
Conclusions: Our results showed that baclofen antagonized the effects of chronic stress on morphine-induced CPP. These findings suggest the potential clinical utility of GABA(B) receptor-positive modulators as an anti-addiction agent in people suffering from chronic stress.
Figures
References
-
- Babb JA, Masini CV, Day HE, Campeau S. Sex differences in activated corticotropin-releasing factor neurons within stress-related neurocircuitry and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical axis hormones following restraint in rats. Neuroscience. 2013;234:40–52. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.051. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

