Neuronal damage using fluoro-Jade B histofluorescence and gliosis in the gerbil septum submitted to various durations of cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 23893372
- PMCID: PMC11497893
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-013-9967-y
Neuronal damage using fluoro-Jade B histofluorescence and gliosis in the gerbil septum submitted to various durations of cerebral ischemia
Abstract
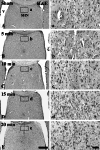
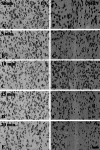
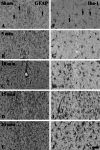
The extent of neuronal damage/death in some brain regions is highly correlated to duration time of transient ischemia. In the present study, we carried out neuronal degeneration/death and glial changes in the septum 4 days after 5, 10, 15, and 20 min of transient cerebral ischemia using gerbils. To examine neuronal damage, Fluoro-Jade B (F-J B, a marker for neuronal degeneration) histofluorescence staining was used. F-J B positive ((+)) cells were detected in the septo-hippocampal nucleus (SHN) of the septum only in the 20 min ischemia-group; the mean number of F-J B(+) neurons was 14.9 ± 2.5/400 μm(2) in a section. Gliosis of astrocytes and microglia was examined using anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and anti-ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1), respectively. In all the ischemia-groups, GFAP- and Iba-1-immunoreactive astrocytes and microglia, respectively, were increased in number, and apparently tended to be increased in their immunoreactivity. Especially, in the 20 min ischemia-group, the number and immunoreactivity of Iba-immunoreactive microglia was highest and strongest in the ischemic SHN 4 days after ischemia-reperfusion. In brief, our findings showed that neuronal damage/death in the SHN occurred and gliosis was apparently increased in the 20 min ischemia-group at 4 days after ischemia-reperfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

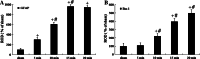
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

