Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 (Ror2) expression creates a poised state of Wnt signaling in renal cancer
- PMID: 23893409
- PMCID: PMC3764835
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.466086
Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 (Ror2) expression creates a poised state of Wnt signaling in renal cancer
Abstract
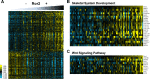
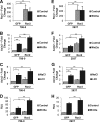
Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 (Ror2) has been identified in an increasing array of tumor types and is known to play a role as an important mediator of Wnt signaling cascades. In this study, we aimed to clarify Ror2 interactions with the Wnt pathways within the context of renal cell carcinoma (RCC). An examination of Ror2 expression in primary human RCC tumors showed a significant correlation with several Wnt signaling genes, including the classical feedback target gene Axin2. We provide evidence that Ror2 expression results in a partially activated state for canonical Wnt signaling through an increased signaling pool of β-catenin, leading to an enhancement of downstream target genes following Wnt3a stimulation in both renal and renal carcinoma-derived cells. Additionally, inhibition of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) with either siRNA or dickkopf decreased the response to Wnt3a stimulation, but no change was seen in the increased β-catenin pool associated with Ror2 expression, suggesting that LRP6 cofactor recruitment is necessary for a Wnt3a-induced signal but that it does not participate in the Ror2 effect on β-catenin signaling. These results highlight a new role for Ror2 in conveying a tonic signal to stabilize soluble β-catenin and create a poised state of enhanced responsiveness to Wnt3a exogenous signals in RCC.
Keywords: Cancer; RCC; Receptor Tyrosine Kinase; Renal Cell Carcinoma; Ror2; Signaling; Wnt Signaling; Wnt3a; β-Catenin.
Figures






References
-
- Li V. S., Ng S. S., Boersema P. J., Low T. Y., Karthaus W. R., Gerlach J. P., Mohammed S., Heck A. J., Maurice M. M., Mahmoudi T., Clevers H. (2012) Wnt signaling through inhibition of β-catenin degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell 149, 1245–1256 - PubMed
-
- Angers S., Moon R. T. (2009) Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 468–477 - PubMed
-
- Wright T. M., Brannon A. R., Gordan J. D., Mikels A. J., Mitchell C., Chen S., Espinosa I., van de Rijn M., Pruthi R., Wallen E., Edwards L., Nusse R., Rathmell W. K. (2009) Ror2, a developmentally regulated kinase, promotes tumor growth potential in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 28, 2513–2523 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Edris B., Espinosa I., Mühlenberg T., Mikels A., Lee C. H., Steigen S. E., Zhu S., Montgomery K. D., Lazar A. J., Lev D., Fletcher J. A., Beck A. H., West R. B., Nusse R., van de Rijn M. (2012) ROR2 is a novel prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target in leiomyosarcoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumour. J. Pathol. 227, 223–233 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 CA009156/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25GM055336/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA132543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM055336/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31CA132543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA071341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121781/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007092/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069768-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069768/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008719/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-CA009156/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 ES007126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

