Trypanosome Letm1 protein is essential for mitochondrial potassium homeostasis
- PMID: 23893410
- PMCID: PMC3772241
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.495119
Trypanosome Letm1 protein is essential for mitochondrial potassium homeostasis
Abstract
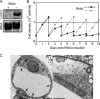
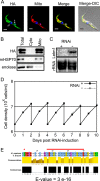
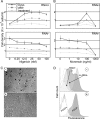
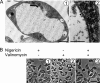
Letm1 is a conserved protein in eukaryotes bearing energized mitochondria. Hemizygous deletion of its gene has been implicated in symptoms of the human disease Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Studies almost exclusively performed in opisthokonts have attributed several roles to Letm1, including maintaining mitochondrial morphology, mediating either calcium or potassium/proton antiport, and facilitating mitochondrial translation. We address the ancestral function of Letm1 in the highly diverged protist and significant pathogen, Trypanosoma brucei. We demonstrate that Letm1 is involved in maintaining mitochondrial volume via potassium/proton exchange across the inner membrane. This role is essential in the vector-dwelling procyclic and mammal-infecting bloodstream stages as well as in Trypanosoma brucei evansi, a form of the latter stage lacking an organellar genome. In the pathogenic bloodstream stage, the mitochondrion consumes ATP to maintain an energized state, whereas that of T. brucei evansi also lacks a conventional proton-driven membrane potential. Thus, Letm1 performs its function in different physiological states, suggesting that ion homeostasis is among the few characterized essential pathways of the mitochondrion at this T. brucei life stage. Interestingly, Letm1 depletion in the procyclic stage can be complemented by exogenous expression of its human counterpart, highlighting the conservation of protein function between highly divergent species. Furthermore, although mitochondrial translation is affected upon Letm1 ablation, it is an indirect consequence of K(+) accumulation in the matrix.
Keywords: Bioenergetics; Letm1; Mitochondria; Potassium Transport; Translation; Trypanosome.
Figures



References
-
- Nowikovsky K., Froschauer E. M., Zsurka G., Samaj J., Reipert S., Kolisek M., Wiesenberger G., Schweyen R. J. (2004) The LETM1/YOL027 gene family encodes a factor of the mitochondrial K+ homeostasis with a potential role in the Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 30307–30315 - PubMed
-
- Schlickum S., Moghekar A., Simpson J. C., Steglich C., O'Brien R. J., Winterpacht A., Endele S. U. (2004) LETM1, a gene deleted in Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome, encodes an evolutionarily conserved mitochondrial protein. Genomics 83, 254–261 - PubMed
-
- Dimmer K. S., Navoni F., Casarin A., Trevisson E., Endele S., Winterpacht A., Salviati L., Scorrano L. (2008) LETM1, deleted in Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome is required for normal mitochondrial morphology and cellular viability. Hum. Mol. Genet. 17, 201–214 - PubMed
-
- Endele S., Fuhry M., Pak S. J., Zabel B. U., Winterpacht A. (1999) LETM1, a novel gene encoding a putative EF-hand Ca2+-binding protein, flanks the Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS) critical region and is deleted in most WHS patients. Genomics 60, 218–225 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

