Characterization of the myometrial transcriptome in women with an arrest of dilatation during labor
- PMID: 23893668
- PMCID: PMC4183453
- DOI: 10.1515/jpm-2013-0086
Characterization of the myometrial transcriptome in women with an arrest of dilatation during labor
Abstract
Objective: The molecular basis of failure to progress in labor is poorly understood. This study was undertaken to characterize the myometrial transcriptome of patients with an arrest of dilatation (AODIL).
Study design: Human myometrium was prospectively collected from women in the following groups: (1) spontaneous term labor (TL; n=29) and (2) arrest of dilatation (AODIL; n=14). Gene expression was characterized using Illumina® HumanHT-12 microarrays. A moderated Student's t-test and false discovery rate adjustment were used for analysis. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) of selected genes was performed in an independent sample set. Pathway analysis was performed on the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway database using Pathway Analysis with Down-weighting of Overlapping Genes (PADOG). The MetaCore knowledge base was also searched for pathway analysis.
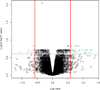
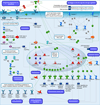
Results: (1) Forty-two differentially expressed genes were identified in women with an AODIL; (2) gene ontology analysis indicated enrichment of biological processes, which included regulation of angiogenesis, response to hypoxia, inflammatory response, and chemokine-mediated signaling pathway. Enriched molecular functions included transcription repressor activity, heat shock protein (Hsp) 90 binding, and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity; (3) MetaCore analysis identified immune response chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) signaling, muscle contraction regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity in endothelial cells, and triiodothyronine and thyroxine signaling as significantly overrepresented (false discovery rate <0.05); (4) qRT-PCR confirmed the overexpression of Nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3); hypoxic ischemic factor 1A (HIF1A); Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2); angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4); ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1, motif 9 (ADAMTS9); G protein-coupled receptor 4 (GPR4); metallothionein 1A (MT1A); MT2A; and selectin E (SELE) in an AODIL.
Conclusion: The myometrium of women with AODIL has a stereotypic transcriptome profile. This disorder has been associated with a pattern of gene expression involved in muscle contraction, an inflammatory response, and hypoxia. This is the first comprehensive and unbiased examination of the molecular basis of an AODIL.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of the myometrial transcriptome and biological pathways of spontaneous human labor at term.J Perinat Med. 2010 Nov;38(6):617-43. doi: 10.1515/jpm.2010.097. Epub 2010 Jul 14. J Perinat Med. 2010. PMID: 20629487 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular signature of an arrest of descent in human parturition.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011 Feb;204(2):177.e15-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.09.025. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011. PMID: 21284969 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in pregnant human myometrium.J Physiol. 1999 Dec 15;521 Pt 3(Pt 3):705-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00705.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10601500 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of endocrine and mechanical signals in the regulation of myometrial functions during pregnancy and labour.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009 May;144 Suppl 1:S2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2009.02.044. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009. PMID: 19299064 Review.
-
β3 Receptor Signaling in Pregnant Human Myometrium Suggests a Role for β3 Agonists as Tocolytics.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 17;13(6):1005. doi: 10.3390/biom13061005. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37371585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical chorioamnionitis at term I: microbiology of the amniotic cavity using cultivation and molecular techniques.J Perinat Med. 2015 Jan;43(1):19-36. doi: 10.1515/jpm-2014-0249. J Perinat Med. 2015. PMID: 25720095 Free PMC article.
-
Vaginal progesterone, but not 17α-hydroxyprogesterone caproate, has antiinflammatory effects at the murine maternal-fetal interface.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Dec;213(6):846.e1-846.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2015.08.010. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015. PMID: 26264823 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering maternal-fetal cross-talk in the human placenta during parturition using single-cell RNA sequencing.Sci Transl Med. 2024 Jan 10;16(729):eadh8335. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adh8335. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Sci Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38198568 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational tissue transcriptomics in term and preterm human pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Genomics. 2015 Jun 5;8:27. doi: 10.1186/s12920-015-0099-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26044726 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced force increase (HIFI) is a novel mechanism underlying the strengthening of labor contractions, produced by hypoxic stresses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 4;112(31):9763-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503497112. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26195731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACOG Practice Bulletin Number 49, December 2003: Dystocia and augmentation of labor. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102:1445–1454. - PubMed
-
- Adelman DM, Maltepe E, Simon MC. HIF-1 is essential for multilineage hematopoiesis in the embryo. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;475:275–284. - PubMed
-
- Aguan K, Carvajal JA, Thompson LP, Weiner CP. Application of a functional genomics approach to identify differentially expressed genes in human myometrium during pregnancy and labour. Mol Hum Reprod. 2000;6:1141–1145. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GR, Himes JH, Kaufman RB, Mor J, Kogan M. A United States national reference for fetal growth. Obstet Gynecol. 1996;87:163–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
