Basic concepts and principles of stoichiometric modeling of metabolic networks
- PMID: 23893965
- PMCID: PMC4671265
- DOI: 10.1002/biot.201200291
Basic concepts and principles of stoichiometric modeling of metabolic networks
Abstract
Metabolic networks supply the energy and building blocks for cell growth and maintenance. Cells continuously rewire their metabolic networks in response to changes in environmental conditions to sustain fitness. Studies of the systemic properties of metabolic networks give insight into metabolic plasticity and robustness, and the ability of organisms to cope with different environments. Constraint-based stoichiometric modeling of metabolic networks has become an indispensable tool for such studies. Herein, we review the basic theoretical underpinnings of constraint-based stoichiometric modeling of metabolic networks. Basic concepts, such as stoichiometry, chemical moiety conservation, flux modes, flux balance analysis, and flux solution spaces, are explained with simple, illustrative examples. We emphasize the mathematical definitions and their network topological interpretations.
Keywords: Constraint-based modeling; Flux balance analysis; Flux modes; Metabolism; Optimal solution space.
Copyright © 2013 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
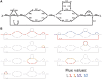
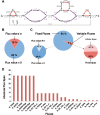
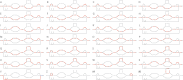
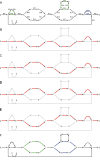
References
-
- Roels JA. Application of macroscopic principles to microbial metabolism. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1980;103:2–59. - PubMed
-
- Cornish-Bowden A. Fundamentals of Enzyme Kinetics. Portland Press Limited; 1995.
-
- Hofmeyr J. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Systems Biology. California Institute of Technology; 2001. Metabolic control analysis in a nutshell; pp. 291–300.
-
- Kholodenko BN, Sauro HM, Westerhoff HV. Control by enzymes, coenzymes and conserved moieties generalization of the connectivity theorem of metabolic control analysis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994;225:179–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

