Characterization of all RND-type multidrug efflux transporters in Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- PMID: 23894076
- PMCID: PMC3831635
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.100
Characterization of all RND-type multidrug efflux transporters in Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Abstract
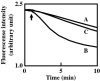
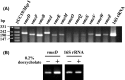
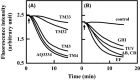
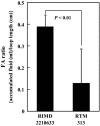
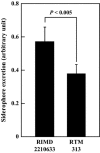
Resistance nodulation cell division (RND)-type efflux transporters play the main role in intrinsic resistance to various antimicrobial agents in many gram-negative bacteria. Here, we estimated 12 RND-type efflux transporter genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Because VmeAB has already been characterized, we cloned the other 11 RND-type efflux transporter genes and characterized them in Escherichia coli KAM33 cells, a drug hypersusceptible strain. KAM33 expressing either VmeCD, VmeEF, or VmeYZ showed increased minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for several antimicrobial agents. Additional four RND-type transporters were functional as efflux pumps only when co-expressed with VpoC, an outer membrane component in V. parahaemolyticus. Furthermore, VmeCD, VmeEF, and VmeYZ co-expressed with VpoC exhibited a broader substrate specificity and conferred higher resistance than that with TolC of E. coli. Deletion mutants of these transporter genes were constructed in V. parahaemolyticus. TM32 (ΔvmeAB and ΔvmeCD) had significantly decreased MICs for many antimicrobial agents and the number of viable cells after exposure to deoxycholate were markedly reduced. Strains in which 12 operons were all disrupted had very low MICs and much lower fluid accumulation in rabbit ileal loops. These results indicate that resistance nodulation cell division-type efflux transporters contribute not only to intrinsic resistance but also to exerting the virulence of V. parahaemolyticus.
Keywords: Drug resistance; RND; V. parahaemolyticus; multidrug efflux transporter.
© 2013 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Aendekerk S, Ghysels B, Cornelis P, Baysse C. Characterization of a new efflux pump, MexGHI-OpmD, from Pseudomonas aeruginosa that confers resistance to vanadium. Microbiology. 2002;148:2371–2381. - PubMed
-
- Bina JE, Provenzano D, Wang C, Bina XR, Mekalanos JJ. Characterization of the Vibrio cholerae vexAB and vexCD efflux systems. Arch. Microbiol. 2006;186:171–181. - PubMed
-
- Buckley AM, Webber MA, Cooles S, Randall LP, Woodward RM, La Ragione MJ, et al. The AcrAB-TolC efflux system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium plays a role in pathogenesis. Cell. Microbiol. 2006;8:847–856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

