Baicalein selectively induces apoptosis in activated lymphocytes and ameliorates concanavalin a-induced hepatitis in mice
- PMID: 23894507
- PMCID: PMC3718678
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069592
Baicalein selectively induces apoptosis in activated lymphocytes and ameliorates concanavalin a-induced hepatitis in mice
Erratum in
-
Correction: baicalein selectively induces apoptosis in activated lymphocytes and ameliorates concanavalin a-induced hepatitis in mice.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 26;10(1):e0117635. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117635. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25622068 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Insufficient apoptosis in activated lymphocytes contributes to the development of autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). Baicalein (BE), a flavonoid originally isolated from the root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, possesses anti-inflammatory properties. However, whether BE can selectively induce apoptosis in activated lymphocytes and exert therapeutic effect on AIH has not been studied.
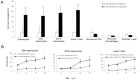
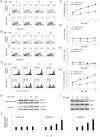
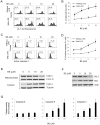
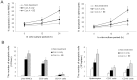
Methodology/principal findings: The pro-apoptotic properties of BE were evaluated in vitro on different types of immune cells, and in vivo effects of BE were examined in a murine model of Concanavalin A (Con A)-induced hepatitis. In vitro treatment with BE resulted in a higher increase in the level of apoptosis in Con A-stimulated murine splenocytes, Con A-stimulated CD3(+) splenocytes, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated CD19(+) splenocytes, and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate/ionomycin-stimulated Jurkat T cells, compared with that in unstimulated naïve ones. Murine bone marrow-derived dentritic cells, peritoneal macrophages, and RAW264.7 cells, either stimulated with LPS or unstimulated, were all insensitive to the BE-induced apoptosis. BE treatment also led to a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, an increase of cytochrome c release from mitochondria to the cytosol, a decrease in the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax, and activation of caspase-9,-3 in Con A-stimulated CD3(+) splenocytes and LPS-stimulated CD19(+) splenocytes, while showing no impact on Fas/FasL expressions and caspase-8 activation. In vivo administration of BE alleviated Con A-induced liver injury, suppressed serum level of TNF-α and IFN-γ, and reduced liver infiltration of mononuclear cells (MNCs). Furthermore, BE treatment increased the incidences of apoptosis in liver-infiltrating MNCs and splenocytes, as well as in CD3(+) and CD19(+) splenocytes. When liver MNCs and splenocytes from BE-treated mice were cultured in vitro for 24 h, they exhibited marked increase in apoptosis compared to vehicle-treated control.
Conclusions/significance: The present study demonstrates the ability of BE to promote apoptosis in activated lymphocytes through mitochondrial pathway and its potential use in the treatment of AIH.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of endogenous catecholamines on apoptosis of Con A-activated lymphocytes of rats.J Neuroimmunol. 2007 Dec;192(1-2):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2007.09.012. Epub 2007 Oct 24. J Neuroimmunol. 2007. PMID: 17920695
-
Selective triggering of apoptosis of concanavalin A-activated T cells by fraxinellone for the treatment of T-cell-dependent hepatitis in mice.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jun 1;77(11):1717-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.03.002. Epub 2009 Mar 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19428326
-
Concanavalin-A as a Model for Induction of Murine Autoimmune Hepatitis: Role of TNF-α and NF-κβ During The Acute Phase.Egypt J Immunol. 2020 Jun;27(2):19-30. Egypt J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33548974
-
Immune mechanisms of Concanavalin A model of autoimmune hepatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jan 14;18(2):119-25. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i2.119. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22253517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of Concanavalin A induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Jan;102:108411. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108411. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34891001 Review.
Cited by
-
Activated farnesoid X receptor attenuates apoptosis and liver injury in autoimmune hepatitis.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Oct;12(4):5821-7. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4159. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26238153 Free PMC article.
-
Developing an Absorption-Based Quality Control Method for Hu-Gan-Kang-Yuan Capsules by UFLC-QTOF-MS/MS Screening and HPLC-DAD Quantitative Determination.Molecules. 2016 May 18;21(5):592. doi: 10.3390/molecules21050592. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27213308 Free PMC article.
-
Protective and therapeutic effects of Scutellaria baicalensis and its main active ingredients baicalin and baicalein against natural toxicities and physical hazards: a review of mechanisms.Daru. 2022 Dec;30(2):351-366. doi: 10.1007/s40199-022-00443-x. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Daru. 2022. PMID: 35870110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs associated with a mouse model of concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis: preliminary screening and comprehensive functional analysis.FEBS Open Bio. 2020 Nov;10(11):2350-2362. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12981. Epub 2020 Oct 14. FEBS Open Bio. 2020. PMID: 32965791 Free PMC article.
-
BA-j as a novel CDK1 inhibitor selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells by regulating ROS.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 2;5:13626. doi: 10.1038/srep13626. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26330167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manns MP, Czaja AJ, Gorham JD, Krawitt EL, Mieli-Vergani G, et al. (2010) Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 51: 2193–2213. - PubMed
-
- Heneghan MA, McFarlane IG (2002) Current and novel immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 35: 7–13. - PubMed
-
- Giovannetti A, Pierdominici M, Di Iorio A, Cianci R, Murdaca G, et al. (2008) Apoptosis in the homeostasis of the immune system and in human immune mediated diseases. Curr Pharm Des 14: 253–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

