A dual role for SAGA-associated factor 29 (SGF29) in ER stress survival by coordination of both histone H3 acetylation and histone H3 lysine-4 trimethylation
- PMID: 23894581
- PMCID: PMC3720948
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070035
A dual role for SAGA-associated factor 29 (SGF29) in ER stress survival by coordination of both histone H3 acetylation and histone H3 lysine-4 trimethylation
Abstract
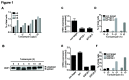
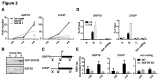
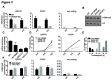
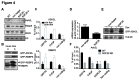
The SGF29 protein binds to tri-methylated lysine-4 of histone H3 (H3K4me3), which is a histone modification associated with active promoters. Human SGF29 is a subunit of the histone acetyltransferase module of the SAGA (Spt-Ada-Gcn5 acetyltransferase) and ATAC (Ada-Two-A-containing 2A) co-activator complexes. Previous work revealed that the SAGA complex is recruited to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress target genes and required for their induction. Here, we report the involvement of SGF29 in the survival of human cells from ER stress. SGF29 knockdown results in impaired transcription of the ER stress genes GRP78 and CHOP. Besides histone H3K14 acetylation, we find that SGF29 is also required for the maintenance of H3K4me3 at these genes, which is already present prior to ER stress. Reduced levels of H3K4me3 in the absence of SGF29 correlate with a decreased association of ASH2L, which is a core component of the SET1/MLL complexes, to GFP78 and CHOP. In conclusion, our results suggest that the H3K4me3-binding protein SGF29 plays a central and dual role in the ER stress response. Prior to ER stress, the protein coordinates H3K4me3 levels, thereby maintaining a 'poised' chromatin state on ER stress target gene promoters. Following ER stress induction, SGF29 is required for increased H3K14 acetylation on these genes, which then results in full transcriptional activation, thereby promoting cell survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Brownell JE, Zhou J, Ranalli T, Kobayashi R, Edmondson DG et al. (1996) Tetrahymena histone acetyltransferase A: a homolog to yeast Gcn5p linking histone acetylation to gene activation. Cell 84: 843-851. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81063-6. PubMed: 8601308. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ernst J, Kheradpour P, Mikkelsen TS, Shoresh N, Ward LD et al. (2011) Mapping and analysis of chromatin state dynamics in nine human cell types. Nature 473: 43-49. doi:10.1038/nature09906. PubMed: 21441907. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Millar CB, Grunstein M (2006) Genome-wide patterns of histone modifications in yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 657-666. doi:10.1038/nrm1986. PubMed: 16912715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Karmodiya K, Krebs AR, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Kimura H, Tora L (2012) H3K9 and H3K14 acetylation co-occur at many gene regulatory elements, while H3K14ac marks a subset of inactive inducible promoters in mouse embryonic stem cells. BMC Genomics 13: 424. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-13-424. PubMed: 22920947. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ruthenburg AJ, Allis CD, Wysocka J (2007) Methylation of lysine 4 on histone H3: intricacy of writing and reading a single epigenetic mark. Mol Cell 25: 15-30. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.12.014. PubMed: 17218268. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

