The role of FOXP3 in disease progression in colorectal cancer patients
- PMID: 23894712
- PMCID: PMC3716747
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.24521
The role of FOXP3 in disease progression in colorectal cancer patients
Abstract
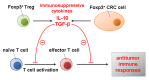
The transcription factor forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) has been identified as a marker of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells and is a key determinant of their immunosuppressive functions. FOXP3 has indeed been shown to limit antitumor immune responses during tumor progression. In addition, by expressing FOXP3, tumor cells may evade effector T-cell responses.
Keywords: FOXP3; colorectal cancer; prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of Foxp3 in colorectal cancer but not in Treg cells correlates with disease progression in patients with colorectal cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053630. Epub 2013 Jan 30. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23382847 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of CD8+CD25+Foxp3+ suppressive T cells in colorectal cancer tissue.Gut. 2009 Apr;58(4):520-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.158824. Epub 2008 Nov 20. Gut. 2009. PMID: 19022917
-
Determination of a CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+T cells subset in Egyptian Colorectal Cancer Patients.Egypt J Immunol. 2021 Jul;28(3):145-156. Egypt J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34453786
-
Epigenetic Variability of CD4+CD25+ Tregs Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017 Apr;52(2):260-272. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8590-3. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27687891 Review.
-
FOXP3+ Tregs: heterogeneous phenotypes and conflicting impacts on survival outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer.Immunol Res. 2015 Mar;61(3):338-47. doi: 10.1007/s12026-014-8616-y. Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25608795 Review.
Cited by
-
The Application of Gene Expression Profiling in Predictions of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer Patients.Biomedicines. 2018 Mar 2;6(1):27. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6010027. Biomedicines. 2018. PMID: 29498671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory T cells inhibit FoxP3 to increase the population of tumor initiating cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 29;150(7):373. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05892-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39073490 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin B receptor expression in malignant gliomas: the perivascular immune escape mechanism of gliomas.J Neurooncol. 2016 Mar;127(1):23-32. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-2017-5. Epub 2015 Dec 8. J Neurooncol. 2016. PMID: 26645886
-
Analysis of frequency changes in CD8+ regulatory T cell subsets in peripheral blood of individuals with type 1 diabetes.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Dec 19;16(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01549-9. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39695694 Free PMC article.
-
Foxp3 expression in CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells promotes development of colorectal cancer by inhibiting tumor immunity.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Oct;36(5):677-682. doi: 10.1007/s11596-016-1644-1. Epub 2016 Oct 18. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27752897
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
