Clinical analysis of genome next-generation sequencing data using the Omicia platform
- PMID: 23895124
- PMCID: PMC3828661
- DOI: 10.1586/14737159.2013.811907
Clinical analysis of genome next-generation sequencing data using the Omicia platform
Abstract
Aims: Next-generation sequencing is being implemented in the clinical laboratory environment for the purposes of candidate causal variant discovery in patients affected with a variety of genetic disorders. The successful implementation of this technology for diagnosing genetic disorders requires a rapid, user-friendly method to annotate variants and generate short lists of clinically relevant variants of interest. This report describes Omicia's Opal platform, a new software tool designed for variant discovery and interpretation in a clinical laboratory environment. The software allows clinical scientists to process, analyze, interpret and report on personal genome files.
Materials & methods: To demonstrate the software, the authors describe the interactive use of the system for the rapid discovery of disease-causing variants using three cases.
Results & conclusion: Here, the authors show the features of the Opal system and their use in uncovering variants of clinical significance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
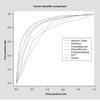
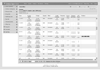




References
-
-
Lupski JR, Reid JG, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, et al. Whole-genome sequencing in a patient with Charcot–Marie–Tooth neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;362(13):1181–1191. • Landmark publication describing the discovery of a causative variant for a Mendelian disorder using whole-genome sequencing.
-
-
-
Ng SB, Buckingham KJ, Lee C, et al. Exome sequencing identifies the cause of a mendelian disorder. Nat. Genet. 2010;42(1):30–35. • Landmark publication describing the discovery of a causative variant for a Mendelian disorder using exome sequencing.
-
Websites
-
- OMIM. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim.
-
- PharmGKB. http://www.pharmgkb.org/
-
- 1000 Genomes. www.1000genomes.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
