Thrombospondin-1 modulates VEGF signaling via CD36 by recruiting SHP-1 to VEGFR2 complex in microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 23896411
- PMCID: PMC3765061
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-482315
Thrombospondin-1 modulates VEGF signaling via CD36 by recruiting SHP-1 to VEGFR2 complex in microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
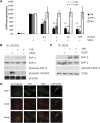
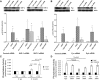
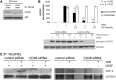
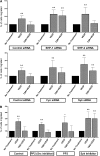
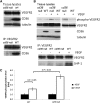
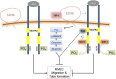
Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) inhibits growth factor signaling at the receptor level in microvascular endothelial cells (MVEC), and CD36 has been suggested to be involved in this inhibition, but the mechanisms are not known. We hypothesized that CD36-TSP-1 interaction recruits Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP)-1 to the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) signaling complex and attenuates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling. Western blots of anti-CD36 and anti-VEGFR2 immunoprecipitates from VEGF-treated MVEC showed that exposure of the cells to a recombinant protein containing the CD36 binding domain of thrombospondin-1 (known as the TSR domain) induced association of SHP-1 with the VEGFR2/CD36 signaling complex and thereby suppressed VEGFR2 phosphorylation. SHP-1 phosphatase activity was increased in immunoprecipitated VEGFR2 complexes from TSR-treated cells. Silencing CD36 expression in MVEC by small interfering RNA (siRNA) or genetic deletion of cd36 in mice showed that TSR-induced SHP-1/VEGFR2 complex formation required CD36 in vitro and in vivo. Silencing SHP-1 expression in MVEC by siRNA abrogated TSR-mediated inhibition of VEGFR2 phosphorylation as well as TSR-mediated inhibition of VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration and tube formation. These studies reveal a SHP-1-mediated antiangiogenic pathway induced by CD36-TSP-1 interaction that inhibits VEGFR2 signaling and they provide a novel target to modulate angiogenesis therapeutically.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Priming of the vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway by thrombospondin-1, CD36, and spleen tyrosine kinase.Blood. 2011 Apr 28;117(17):4658-66. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-305284. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21378271 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of antiangiogenic thrombospondin-1 type 1 repeat domain interactions with CD36.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Jul;33(7):1655-62. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301523. Epub 2013 May 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23640500 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin-1 modulates vascular endothelial growth factor activity at the receptor level.FASEB J. 2009 Oct;23(10):3368-76. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-131649. Epub 2009 Jun 15. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19528255 Free PMC article.
-
CD36: a critical anti-angiogenic receptor.Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:s874-82. doi: 10.2741/1168. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957861 Review.
-
CD36-TSP-HRGP interactions in the regulation of angiogenesis.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(35):3559-67. doi: 10.2174/138161207782794185. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 18220792 Review.
Cited by
-
CD36 and CD97 in Pancreatic Cancer versus Other Malignancies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 6;21(16):5656. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165656. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32781778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial Cell Behavior Is Determined by Receptor Clustering Induced by Thrombospondin-1.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 29;9:664696. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.664696. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SASH1 promotes melanin synthesis and migration via suppression of TGF-β1 secretion in melanocytes resulting in pathologic hyperpigmentation.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Feb 10;16(7):1264-1273. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.38415. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32174800 Free PMC article.
-
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Induced Brain Injury Is Mediated by the Interleukin-12 Receptor in Rats.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020 Apr 1;16:891-900. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S228773. eCollection 2020. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020. PMID: 32308392 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Capillary Regression is not Dependent on Reducing VEGF Expression.Microcirculation. 2016 Feb;23(2):146-56. doi: 10.1111/micc.12263. Microcirculation. 2016. PMID: 26660949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clemetson KJ, Pfueller SL, Luscher EF, Jenkins CS. Isolation of the membrane glycoproteins of human blood platelets by lectin affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977;464(3):493–508. - PubMed
-
- Silverstein RL, Baird M, Lo SK, Yesner LM. Sense and antisense cDNA transfection of CD36 (glycoprotein IV) in melanoma cells. Role of CD36 as a thrombospondin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(23):16607–16612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

